Species of Thailand
Brown-cheeked fulvetta
Alcippe poioicephala
Thomas C. Jerdon, 1844
In Thai: นกมุ่นรกตาขาว
The brown-cheeked fulvetta (Alcippe poioicephala) (or brown-cheeked alcippe as the fulvettas proper are not closely related to this bird), is included in the family Alcippeidae. It was earlier also known as the quaker babbler.
This species is one of those retained in the genus Alcippe after the true fulvettas and some others were removed; the group had turned out to unite quite unrelated birds. Its closest relatives are probably the brown fulvetta, and the black-browed fulvetta which was only recently recognized as a distinct species again. The Javan fulvetta and the Nepal fulvetta might also belong into this group.(Pasquet et al. 2006)
The brown-cheeked fulvetta is a resident breeding bird in Bangladesh, India and Southeast Asia. Its habitat is undergrowth in moist forests and scrub jungle. This species, like most babblers, is not migratory, and has short rounded wings and a weak flight.
This babbler builds its nest in a tree, concealed in dense masses of foliage. The normal clutch is two or three eggs.
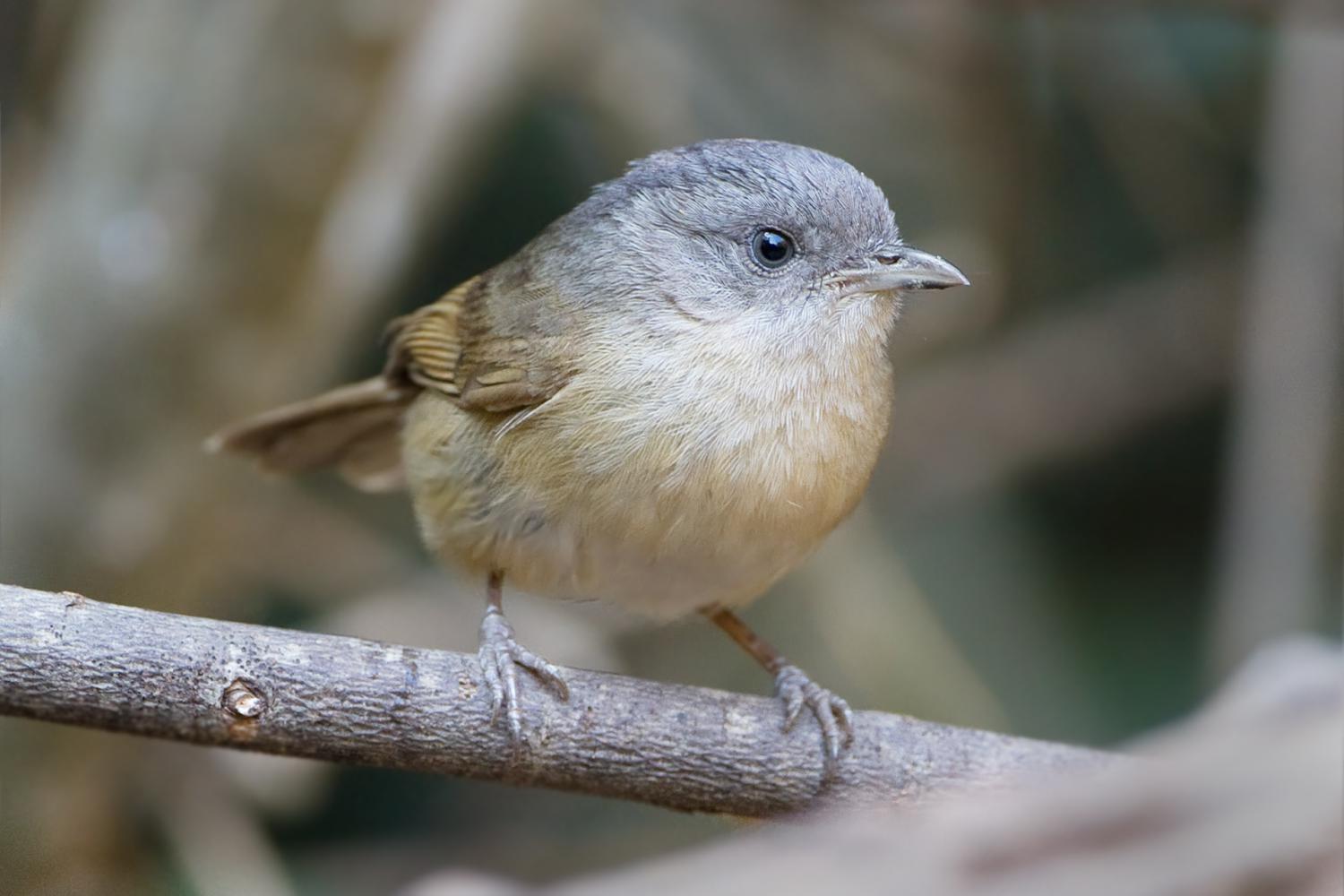
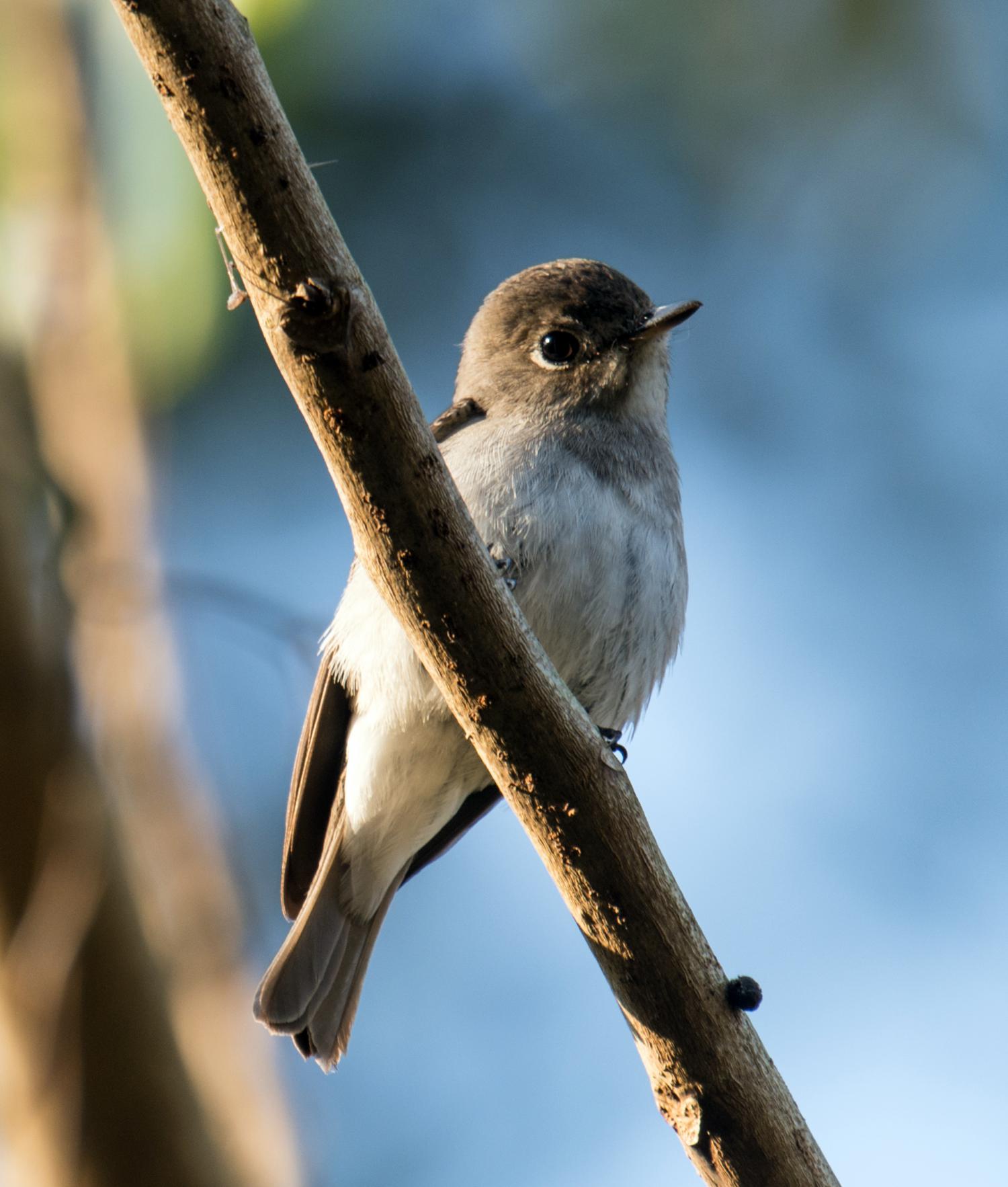
Brown-cheeked fulvetta measures 15 cm including its longish tail. It is brown above and buff, with no patterning on the body or wings. The crown is grey, and the cheeks are dark.
Brown-cheeked fulvettas have short dark bills. Their food is mainly insects and nectar. They can be difficult to observe in the dense vegetation they prefer, but these are vocal birds, and their characteristic calls are often the best indication that these birds are present.
Nesting
The brown-cheeked fulvetta nests from January to June with a peak in January–February. In a study by Anoop Das and Vijayan, a total of 38 nests were found in 50, 000 square metres. The nest is a cup, built with green moss, rootlets, lichen, leaves and grass lined with rootlets and placed in a fork or suspended from the twigs at a mean height of 68.21 cm from ground. Mean nest width was 91.8 mm and depth 48.7 mm.
Clutch size was two to three eggs and the incubation period is 10 ± 2 days and the nestling period is 12 ± 2 days. Hatching success was 55% while the nestling success was 32%. The most preferred plants for nesting were shrubs of the species Lasianthus ciliatus (36%) followed by the Saprosma fragrans (27%) and Thottea siliquosa (23%).
They tended to locate their nests at central position just near the main stem. A principal component analysis of the nest site variables showed nest height, concealment, plant height and canopy cover as the major parameters in nest site selection, explaining 73% cumulative variance. Of these the crucial deciding factors were plant height and canopy cover when the nest sites were compared with the random sites (discriminant function analysis).
Nest success was directly correlated with concealment as it reduces the chance for predation. Nest site selection of this bird thus shows the choice of a particular location for successful nesting, which is a dense evergreen forest with dense shrub cover and without much disturbance.
This article uses material from Wikipedia released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike Licence 3.0. Eventual photos shown in this page may or may not be from Wikipedia, please see the license details for photos in photo by-lines.
Category / Seasonal Status
BCST Category: Recorded in an apparently wild state within the last 50 years
BCST Seasonal status: Resident or presumed resident
Scientific classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Passeriformes
- Family
- Alcippeidae
- Genus
- Alcippe
- Species
- Alcippe poioicephala
Common names
- Thai: นกมุ่นรกตาขาว
Conservation status

Least Concern (IUCN3.1)
Photos
Please help us review the bird photos if wrong ones are used. We can be reached via our contact us page.
Range Map
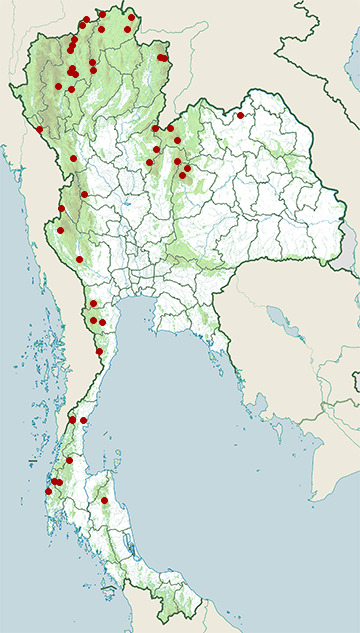
- Chae Son National Park
- Chiang Dao District, Chiang Mai
- Chiang Dao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Chiang Khong District, Chiang Rai
- Doi Inthanon National Park
- Doi Lang
- Doi Pha Hom Pok National Park
- Doi Phu Kha National Park
- Doi Suthep - Pui National Park
- Erawan National Park
- Kaeng Krachan District, Phetchaburi
- Kaeng Krachan National Park
- Kaeng Krung National Park
- Khao Laem National Park
- Khao Luang National Park
- Khao Sok National Park
- Khon San District, Chaiyaphum
- Khun Chae National Park
- Khun Korn Forest Park
- Khun Nan National Park
- Khun Tan District, Chiang Rai
- Kromluang Chumphon Wildlife Sanctuary
- Kui Buri National Park
- Mae Fa Luang District, Chiang Rai
- Mae Moei National Park
- Mae Rim District, Chiang Mai
- Mae Wong National Park
- Mueang Chiang Mai District, Chiang Mai
- Mueang Chumphon District, Chumphon
- Nam Nao National Park
- Pa Sang District, Lamphun
- Pachee River Wildlife Sanctuary
- Pha Daeng National Park
- Phu Hin Rong Kla National Park
- Phu Khiao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Phu Luang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Phu Ruea National Park
- Phu Suan Sai National Park
- Sang Khom District, Udon Thani
- Sri Phang Nga National Park
- Taksin Maharat National Park
- Takua Pa District, Phang Nga
- Thung Salaeng Luang National Park
- Thung Yai Naresuan Wildlife Sanctuary
- Wang Mai Forest Restoration Project


