Species of Thailand
Purple sunbird
Cinnyris asiaticus
John Latham, 1790
In Thai: นกกินปลีดำม่วง
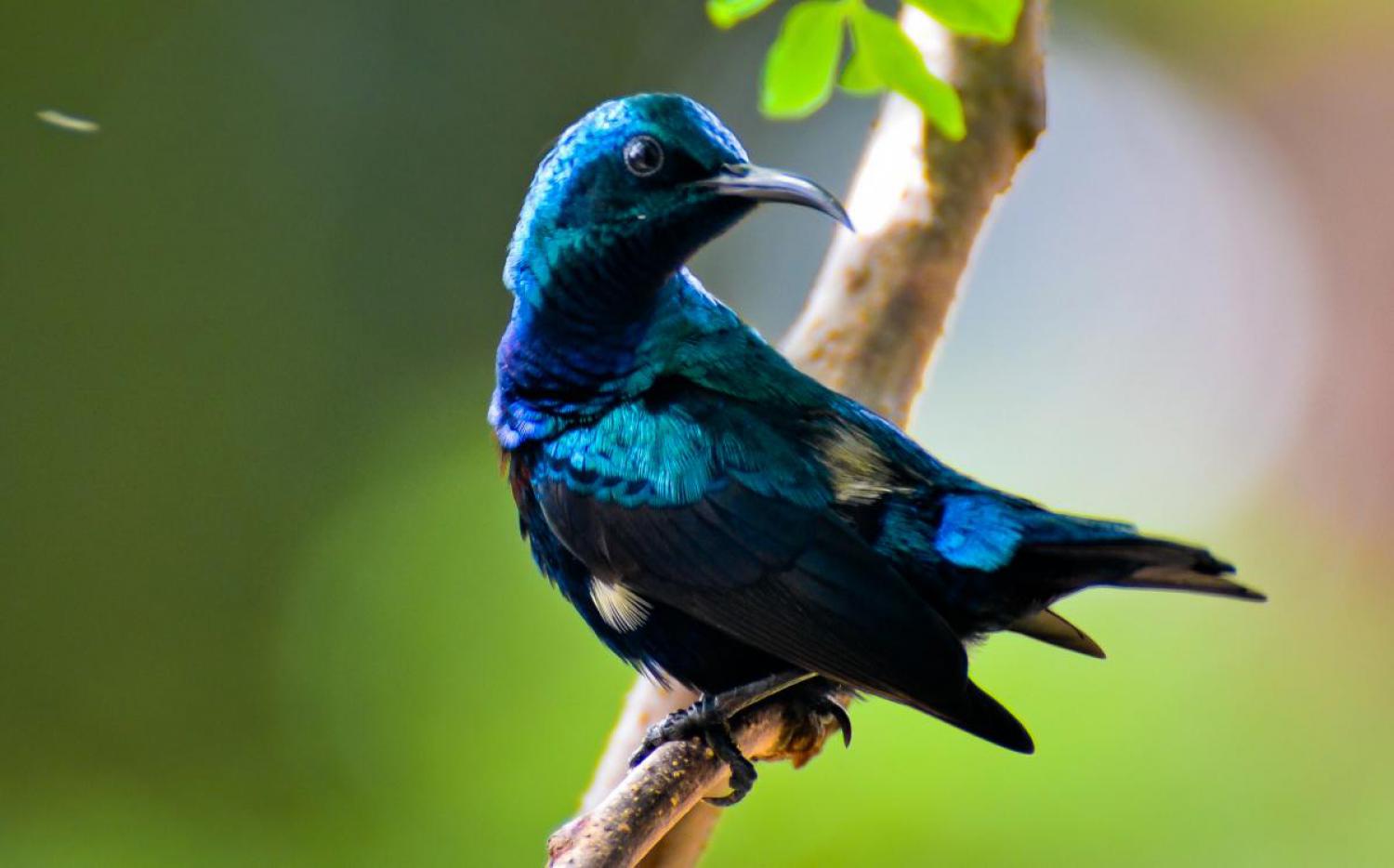
The purple sunbird (Cinnyris asiaticus) is a small bird in the sunbird family found mainly in South and Southeast Asia but extending west into parts of the Arabian peninsula. Like other sunbirds they feed mainly on nectar, although they will also take insects, especially when feeding young. They have a fast and direct flight and can take nectar by hovering like a hummingbird but often perch at the base of flowers. The males can appear all black in harsh sunlight but the purple iridescence is visible on closer observation or under good light conditions. Females are olive above and yellowish below.
Description
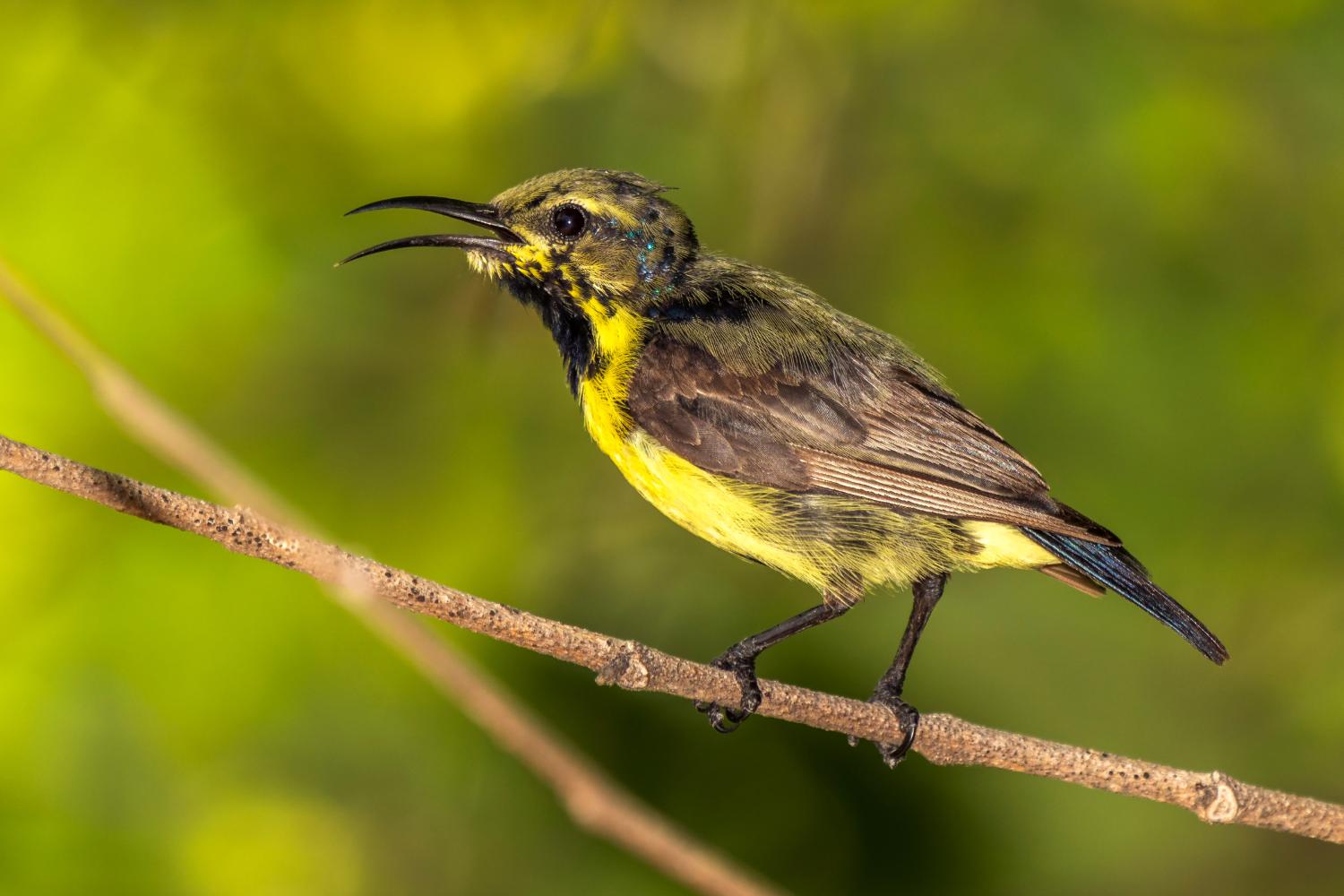
This small sunbird has a relatively short bill, a dark and short square ended tail with distinctive sexual dimorphism. Less than 10 cm long they have a down-curved bill with brush-tipped tubular tongues that aid in nectar feeding. The male is glossy metallic bluish to purplish black on the upper parts with the wings appearing dark brown. The breeding male also has underparts of the same purplish black, but non-breeding males may show a central streak of black on yellow underparts. (Birds in this eclipse plumage were once designated as a species, C. currucaria.) In the breeding plumage, the male can be confused with the syntopic Loten's sunbird which has a long bill and a distinctive broad maroon band on the breast. Breeding males will sometimes show their yellow pectoral tufts in displays. There is a patch of bright blue on the shoulder of breeding males. The maroon shine on the feathers of the collar around the neck is visible mainly during the breeding seasons.
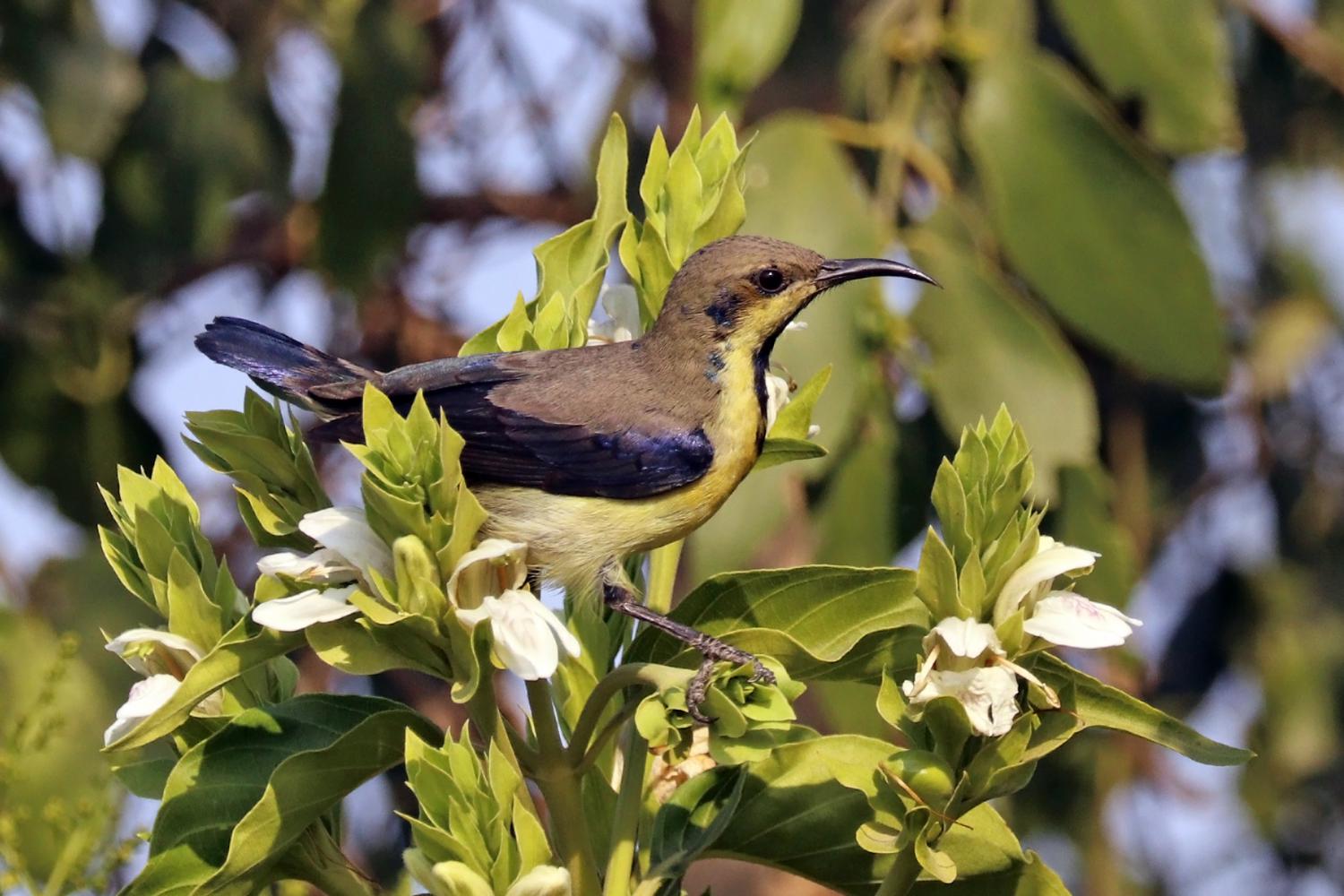
Females are olive brown above with a yellowish underside. There is a pale supercilium beyond the eye. There is a darkish eye stripe. The throat and breast are yellow, becoming pale towards the vent. The outer tail feathers are tipped in white both in the male and female.
They are seen in pairs or small groups and aggregations may be found in gardens with suitable flowers. They feed mainly on nectar but also take fruits and insects. Groups of as many as 40 to 50 individuals have sometimes been noted.
Distribution
The species is distributed widely from West Asia through the Indian subcontinent and into Southeast Asia. They are resident birds in most parts of their range and do not move large distances. They are found in thin forest and garden land, including those in dense urban areas. Local movements are, however, noted especially in the drier parts of northwestern India and Pakistan where they are said to arrive in large numbers before summer.The nominate subspecies is distributed in India east of the desert region and south of the Himalayas extending to the west and south of India and Sri Lanka. They are found mainly on the plains but going up to 2400 m in southern India and up to 1700 m in the Himalayas. The race brevirostris is found in the dry zone from the Arabian Peninsula into Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan until the dry zone of Rajasthan and Gujarat. These may, however, winter south near Goa. This form has a slight tinge of green in the pectoral yellow tufts. The race intermedius extends from the border of Orissa and Andhra Pradesh northwards into Bangladesh, Myanmar and Indochina.
The movements of these birds are not well understood. A male ringed in Bharatpur was recovered in Dehra Dun, 350 km north.
Behaviour and ecology
These birds are very vociferous and will call and will join to mob owls or other predators. The song is rapid rattle followed by ringing, metallic notes. Other call notes include a "chwit" or "chwing!" notes. The primary breeding season is before the Monsoons, April to June in northern India and January to June in Sri Lanka. While feeding they flick their wings. They rarely hover at flowers and usually perch to forage for nectar. They are important pollinators of some plant species such as Butea monosperma, Acacia, Woodfordia and Dendrophthoe. but they sometimes steal nectar by slitting flowers such as Hamelia patens at the base. They are known to feed on small berries such as those of Salvadora persica and cultivated grapes. Insects are sometimes caught by flycatching.
In courtship displays the male raises his head, fans his tail and flutters with partly open wings that expose the pectoral tufts and sings before the female. The nest is a pouch made of cobwebs, thin strips of vegetation, lichens and bark. The entrance hole on the side is often shaded by an overhanging projection. The nest is built almost entirely by the female. The nest material is not woven and most of it is held together by cobwebs. About five to ten days may be taken in the building of the nest. The inner cavity is expanded by the bird by opening its wing and turning around on the inside. In Sri Lanka and in southern India, it sometimes builds its nest by modifying and lining the cobweb structures formed by colonial or 'social' spiders, Stegodyphus sarasinorum (Eresidae). Two eggs are usually laid. The nest is usually suspended from a low branch, often of thorny plants but are sometimes built close to human habitations, attached to wires or other man-made objects and even indoors in an unused toilet. Only the female incubates the eggs which hatch after 15 to 17 days. Males assist in feeding the chicks although females involve themselves to a greater extent, making more trips as the chicks get older.
Sunbirds have been known to live for nearly 22 years in captivity.
This article uses material from Wikipedia released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike Licence 3.0. Eventual photos shown in this page may or may not be from Wikipedia, please see the license details for photos in photo by-lines.
Category / Seasonal Status
BCST Category: Recorded in an apparently wild state within the last 50 years
BCST Seasonal status: Resident or presumed resident
Scientific classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Passeriformes
- Family
- Nectariniidae
- Genus
- Cinnyris
- Species
- Cinnyris asiaticus
Common names
- Thai: นกกินปลีดำม่วง
Synonyms
- Nectarinia mahrattensis
- Arachnechthra intermedia
Conservation status

Least Concern (IUCN3.1)
Photos
Please help us review the bird photos if wrong ones are used. We can be reached via our contact us page.
Range Map
- Ban Hong Non-Hunting Area
- Ban Phai District, Khon Kaen
- Bangkok Province
- Borabue District, Maha Sarakham
- Bueng Boraped Non-Hunting Area
- Chae Hom District, Lampang
- Chatturat District, Chaiyaphum
- Chiang Dao District, Chiang Mai
- Chiang Dao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Chiang Khong District, Chiang Rai
- Chiang Saen District, Chiang Rai
- Doi Inthanon National Park
- Doi Lo District, Chiang Mai
- Doi Pha Hom Pok National Park
- Doi Saket District, Chiang Mai
- Doi Suthep - Pui National Park
- Doi Tao District, Chiang Mai
- Erawan National Park
- Hang Chat District, Lampang
- Huai Chorakhe Mak Reservoir Non-Hunting Area
- Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary
- Huai Nam Dang National Park
- Huai Talat Reservoir Non-Hunting Area
- Kaeng Khoi District, Saraburi
- Kaeng Krachan National Park
- Khao Sam Roi Yot National Park
- Khao Yai National Park
- Khlong Lan National Park
- Khun Chae National Park
- Khun Tan District, Chiang Rai
- Kumphawapi District, Udon Thani
- Laem Pak Bia
- Lam Nam Kok National Park
- Lan Sang National Park
- Mae Ai District, Chiang Mai
- Mae Chan District, Chiang Rai
- Mae Mo District, Lampang
- Mae Ping National Park
- Mae Rim District, Chiang Mai
- Mae Sai District, Chiang Rai
- Mae Sot District, Tak
- Mae Taeng District, Chiang Mai
- Mae Tha, Lampang District, Lampang
- Mae Wong National Park
- Mueang Buriram District, Buriram
- Mueang Chaiyaphum District, Chaiyaphum
- Mueang Chiang Mai District, Chiang Mai
- Mueang Chiang Rai District, Chiang Rai
- Mueang Kamphaeng Phet District, Kamphaeng Phet
- Mueang Khon Kaen District, Khon Kaen
- Mueang Lampang District, Lampang
- Mueang Nakhon Ratchasima District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Mueang Phayao District, Phayao
- Mueang Prachuap Khiri Khan District, Prachuap Khiri Khan
- Mueang Sukhothai District, Sukhothai
- Mueang Surin District, Surin
- Mueang Tak District, Tak
- Nam Nao National Park
- Nam Phong National Park
- Namtok Mae Surin National Park
- Noen Maprang District, Phitsanulok
- Non Thai District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Nong Bong Khai Non-Hunting Area
- Nong Ya Plong District, Phetchaburi
- Op Khan National Park
- Pa Sang District, Lamphun
- Pai District, Mae Hong Son
- Pha Daeng National Park
- Pha Taem National Park
- Phan District, Chiang Rai
- Phatthana Nikhom District, Lopburi
- Phen District, Udon Thani
- Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya District, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya
- Phu Chong Na Yoi National Park
- Phu Wiang National Park
- Pran Buri Forest Park
- Sai Yok District, Kanchanaburi
- Sai Yok National Park
- Sakaerat Environmental Research Station
- San Sai District, Chiang Mai
- Sanam Bin Reservoir Non-Hunting Area
- Sangkhom District, Nong Khai
- Si Thep District, Phetchabun
- Sri Nakarin Dam National Park
- Ta Phraya National Park
- Tha Yang District, Phetchaburi
- Thap Lan National Park
- Thung Yai Naresuan Wildlife Sanctuary
- Wapi Pathum District, Maha Sarakham
- Wat Phai Lom & Wat Ampu Wararam Non-Hunting Area
- Wiang Kaen District, Chiang Rai


