Species of Thailand
Grey peacock-pheasant
Polyplectron bicalcaratum
Carolus Linnaeus, 1758
In Thai: นกแว่นสีเทา
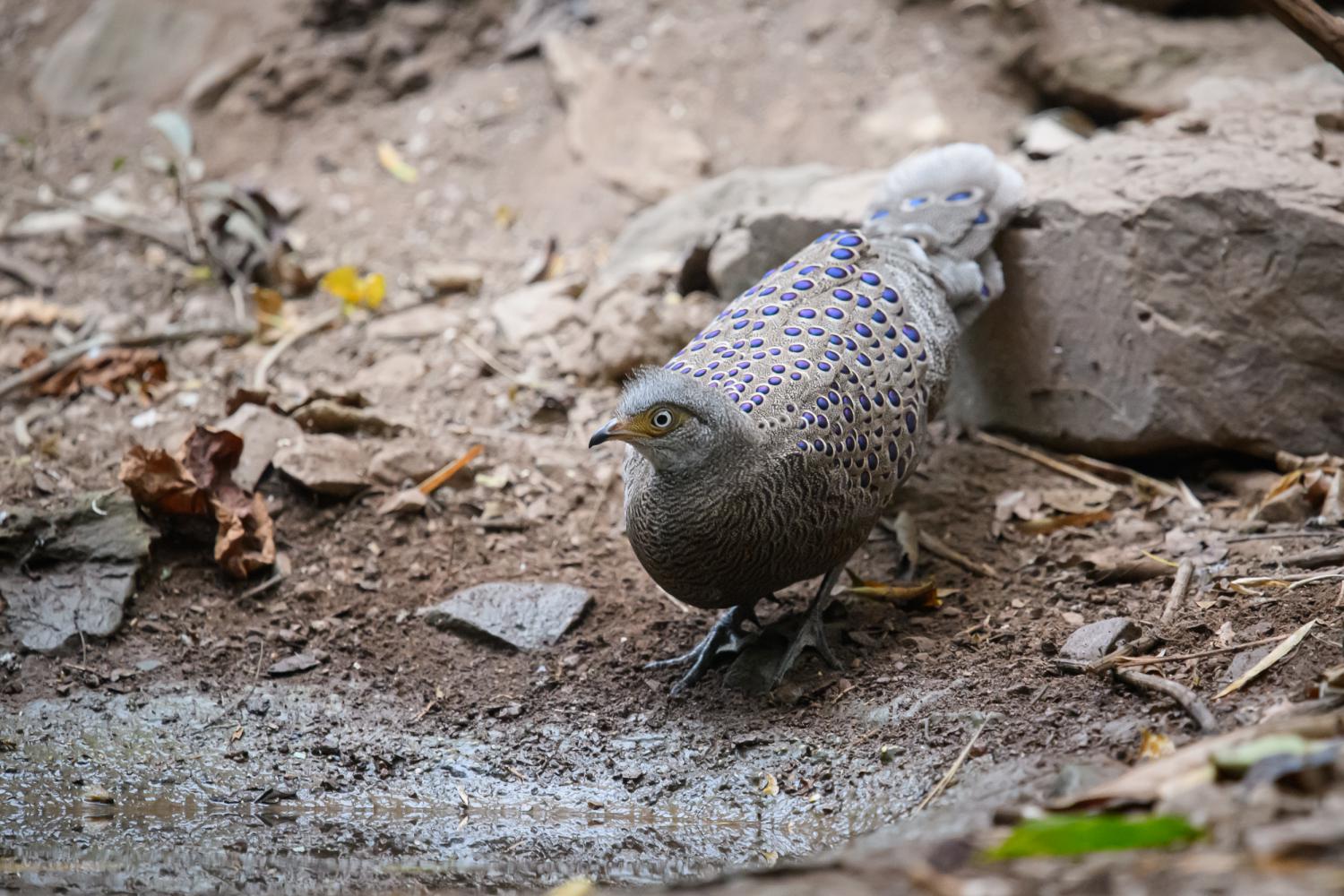
The gray peacock-pheasant (Polyplectron bicalcaratum), also known as Burmese peacock-pheasant, is a large Asian member of the order Galliformes. It is the national bird of Myanmar.
Description
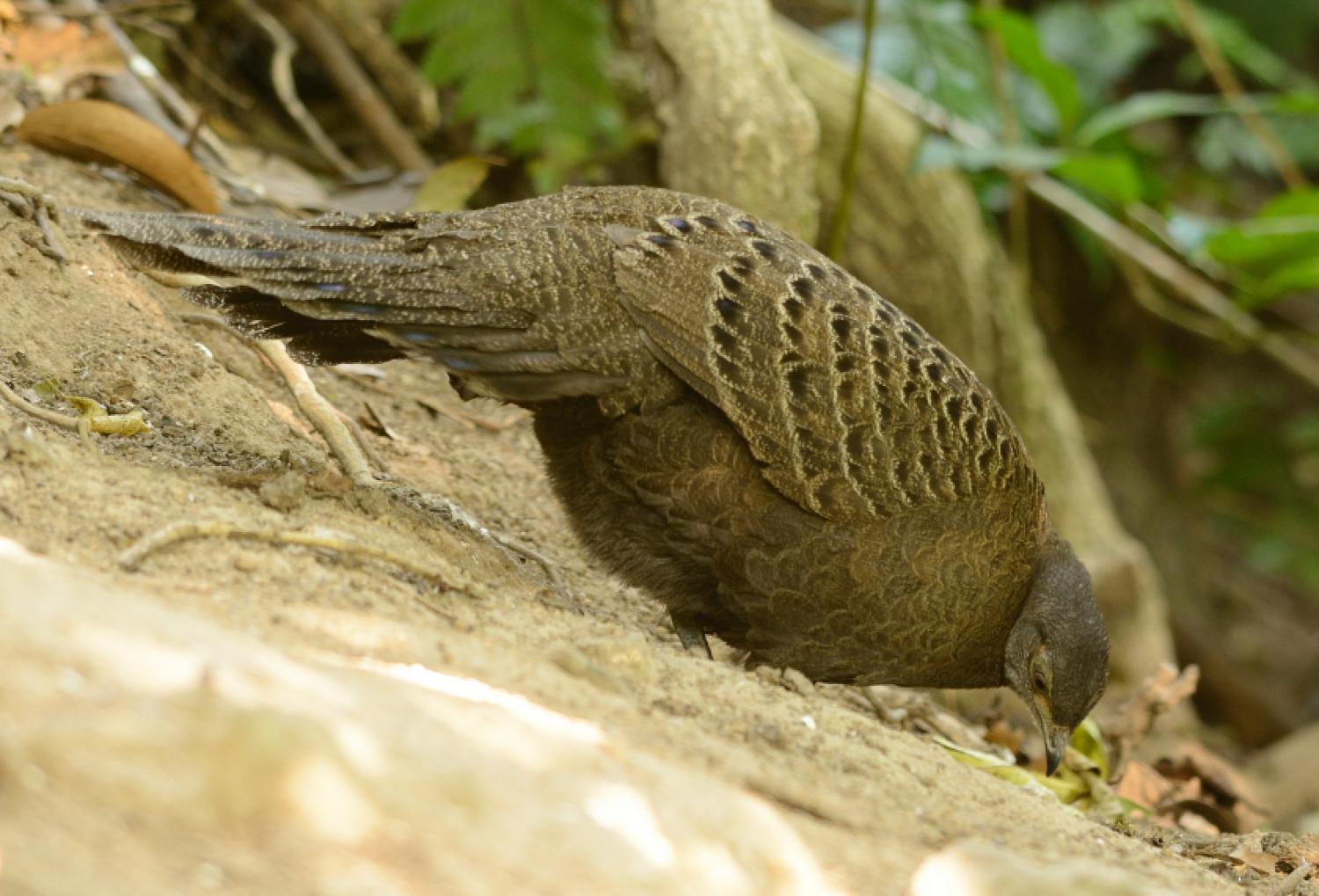
It is a large pheasant, up to 76 cm long and greyish brown with finely spotted green eyespots, an elongated bushy crest, bare pink or yellow facial skin, white throat, and grey iris, bill and legs. The sexes are rather similar, but the female is smaller, darker and less ornamented than the male. The young resemble the female.
Distribution and ecology
The grey peacock-pheasant is distributed in lowland and hill forests of Bangladesh, Northeast India and Southeast Asia, but excluding most of Indochina as well as the entire Malayan Peninsula. The diet consists mainly of seeds, termites, fruits and invertebrates. The female usually lays two eggs.
Status and conservation
Widespread throughout its large range, the grey peacock-pheasant is evaluated as a Species of Least Concern on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. It is listed on CITES Appendix II, restricting trade in wild-caught birds to preserve its stocks.
Systematics
Three subspecies are recognized today as good, while an additional one is of unclear validity:
- P. b. bicalcaratum Linnaeus, 1758 – Common grey peacock-pheasant
- P. b. ghigii Delacour & Jabouille, 1924 – Ghigi's grey peacock-pheasant
- P. b. bailyi Lowe, 1925 – Lowe's grey peacock-pheasant (disputed)
- P. b. bakeri Lowe, 1925 – Northern grey peacock-pheasant
One previous subspecies, the Hainan peacock-pheasant (P. b. katsumatae), has since been given approved species (AS) status by the IOC.
Lowe's grey peacock-pheasant was described from a captive bird of unknown provenance. Similar examples have turned up on occasion, but the validity and – if distinct – home range of this taxon remains unknown. It was theorized to inhabit western Assam or the eastern Himalayas, but this is based on conjecture.
The phylogeny of this species is fairly enigmatic. mtDNA cytochrome b and D-loop as well as the nuclear ovomucoid intron G sequence data confirms that it belongs to a largely Continental Asian clade together with Germain's peacock-pheasant (P. germaini), but also the "brown" southern species bronze-tailed peacock-pheasant (P. chalcurum) and mountain peacock-pheasant (P. inopinatum).
The ovomucin sequence seems to have evolved convergently or with a decreased mutational rate on the grey and the bronze-tailed peacock-pheasant. Though they are quite similar on the molecular level, the distance and interspersed populations of their closest relatives argue against a much more recently shared common ancestry between them versus the other two "northern" peacock-pheasants. Also, the cytochrome b and D-loop data does not support a closer relationship between P. bicalcaratus and P. chalcurum; overall, as it seems the four species' ancestors separated during a very short timespan.
Note however that in the absence of dedicated phylogeographic studies, the molecular data is only of limited value in this species, the most morphologically diverse and widespread peacock-pheasant: There is no data on the origin and number of specimens, but it is unlikely that more than one or two individuals – possibly of captive origin and undeterminable subspecific allocation – were sampled. All that can be reasonably assumed is that the grey peacock-pheasant evolved on mainland Southeast Asia, probably during the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene 3.6-1 million years ago.
References
- Kimball, Rebecca T.; Braun, Edward L.; Ligon, J. David; Lucchini, Vittorio & Randi, Ettore (2001): A molecular phylogeny of the peacock-pheasants (Galliformes: Polyplectron spp.) indicates loss and reduction of ornamental traits and display behaviours. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 73(2): 187–198.
- Lowe, Percy R. (1924): Some notes on the genus Polyplectron. Ibis 67(2): 476–484.
This article uses material from Wikipedia released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike Licence 3.0. Eventual photos shown in this page may or may not be from Wikipedia, please see the license details for photos in photo by-lines.
Category / Seasonal Status
BCST Category: Recorded in an apparently wild state within the last 50 years
BCST Seasonal status: Resident or presumed resident
Scientific classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Galliformes
- Family
- Phasianidae
- Genus
- Polyplectron
- Species
- Polyplectron bicalcaratum
Common names
- English: Grey eacock-pheasant
- Thai: นกแว่นสีเทา
Subspecies
Polyplectron bicalcaratum bailyi, Percy Roycroft Lowe, 1925
Range: Lowe's grey peacock-pheasant (disputed)
Polyplectron bicalcaratum bakeri, Percy Roycroft Lowe, 1925
Range: Northern grey peacock-pheasant
Polyplectron bicalcaratum bicalcaratum, Carolus Linnaeus, 1758
Common name: Common grey peacock-pheasant
Polyplectron bicalcaratum ghigii, Jean Théodore Delacour & Pierre Jabouille, 1924
Common name: Ghigi's grey peacock-pheasant
Conservation status

Least Concern (IUCN3.1)
Photos
Please help us review the bird photos if wrong ones are used. We can be reached via our contact us page.
Range Map
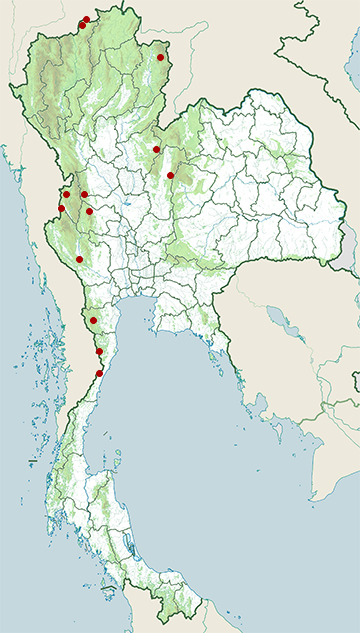
- Doi Lang
- Doi Pha Hom Pok National Park
- Doi Phu Kha National Park
- Erawan National Park
- Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary
- Huai Yang Waterfall National Park
- Kaeng Krachan National Park
- Kui Buri National Park
- Mae Wong National Park
- Phu Hin Rong Kla National Park
- Tat Mok National Park
- Thung Yai Naresuan Wildlife Sanctuary
- Umphang Wildlife Sanctuary

