Species of Thailand
Collared owlet
Glaucidium brodiei
E. Burton, 1836
In Thai: นกเค้าแคระ
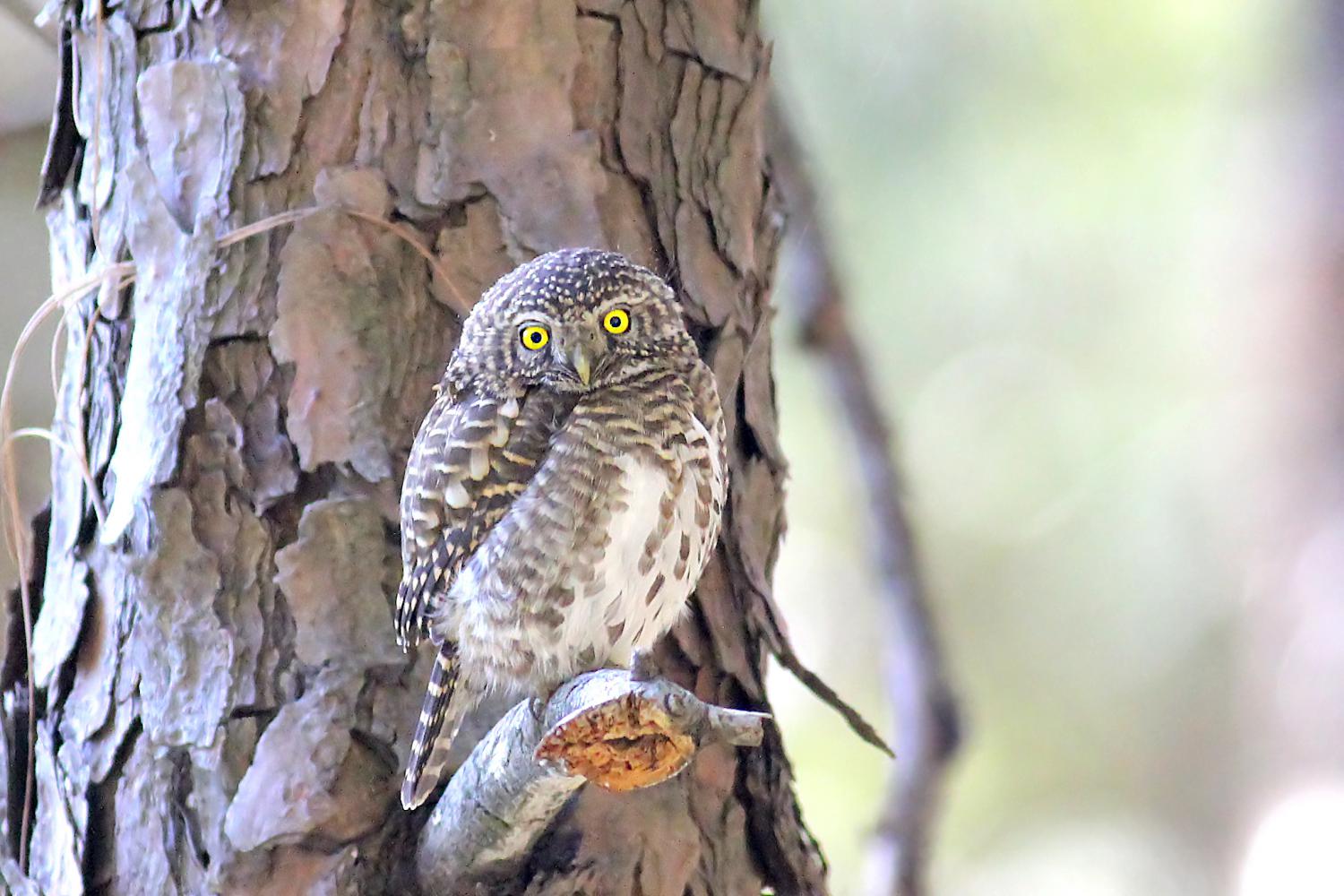
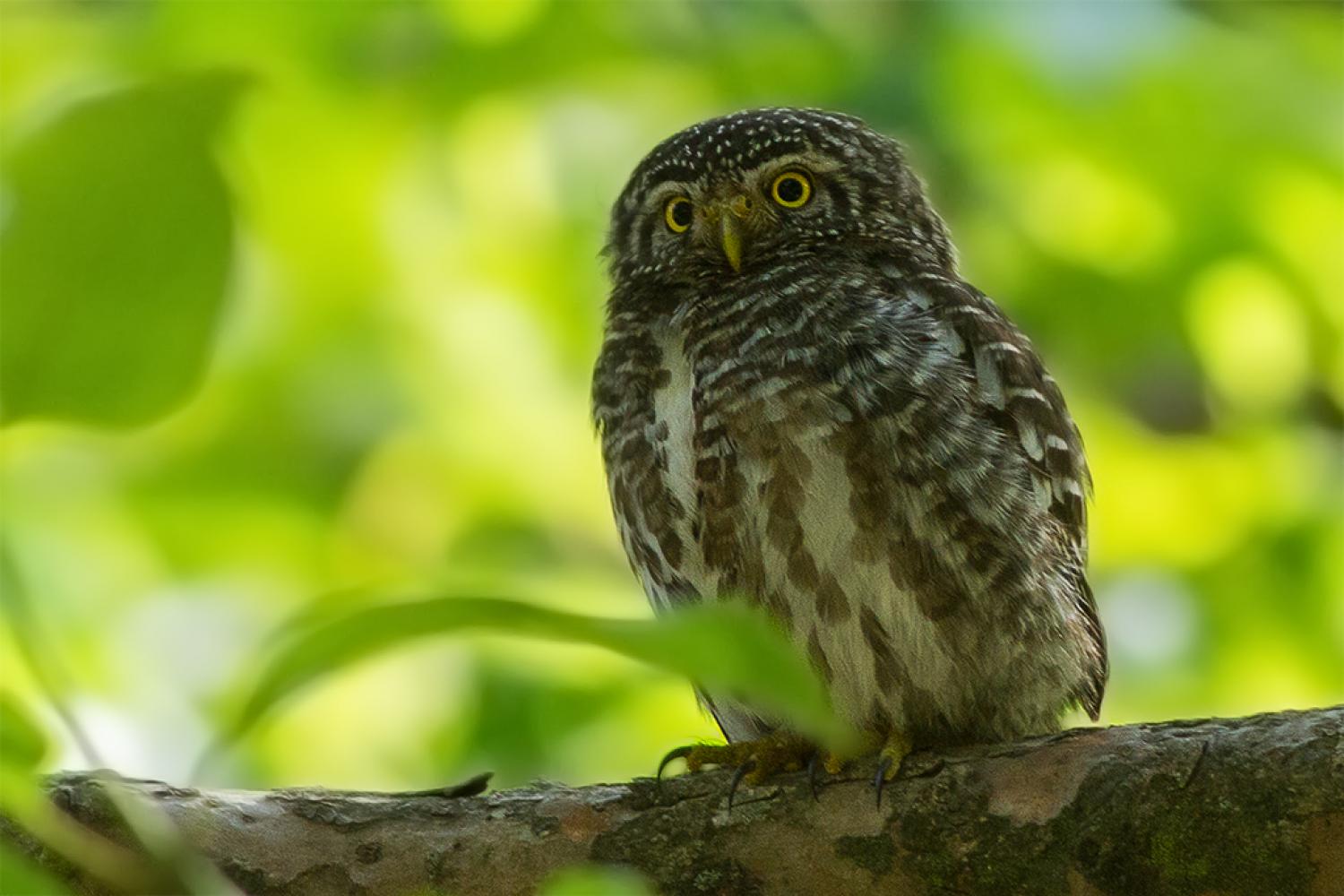
The collared owlet (Glaucidium brodiei), also known as the collared pygmy owl, is a species of owl in the family Strigidae. Its natural habitat is submontane and montane forests with open spaces and is distributed throughout oriental Asia. It is the smallest owl in Asia, at 15 cm and 60 g.
Taxonomy
The collared owlet was first described in 1836 as Noctua brodiei by the English zoologist Edward Burton. It was moved to the genus Glaucidium based on a comparison of mitochondrial DNA sequences and proved to be closely related to the jungle owlet (Glaucidium radiatum) and the Asian barred owlet (Glaucidium cuculoides).
Two subspecies are recognised:
- G. b. brodiei (Burton, 1836) – Himalayas to south China south through Indochina and the Malay Peninsula
- G. b. pardalotum (Swinhoe, 1863) – Taiwan
The Sunda owlet (Glaucidium sylvaticum) was formerly treated as a subspecies of the collared owlet. It was promoted to species status based on the results of a vocalisation study published in 2019.
Description
The collared owlet, being Asia's smallest owl species, measures between 15 and 17 cm. Females are generally larger than the males, weighing approximately 63 grams, whereas males weigh in at 52 grams.
This bird has a grey-brown colour (depending on age-morph) and has a barred back and flanks, while the head is more spotted than barred. They have prominent white eyebrows, vibrant lemon-yellow-coloured eyes and a white throat patch. The chin, center of the breast and belly are mostly white. The pale collar and the two black spots on each side of the nape imitate eye spots and make it seem like the owl is staring at you from behind. This is known as the "occipital face". It has a greyish-brown pale-spotted pectoral band on upper breast and lacks ear-tufts. You can see its tail when in flight, longer than most pygmy owls, and has rapid wingbeats.
Colour morphs
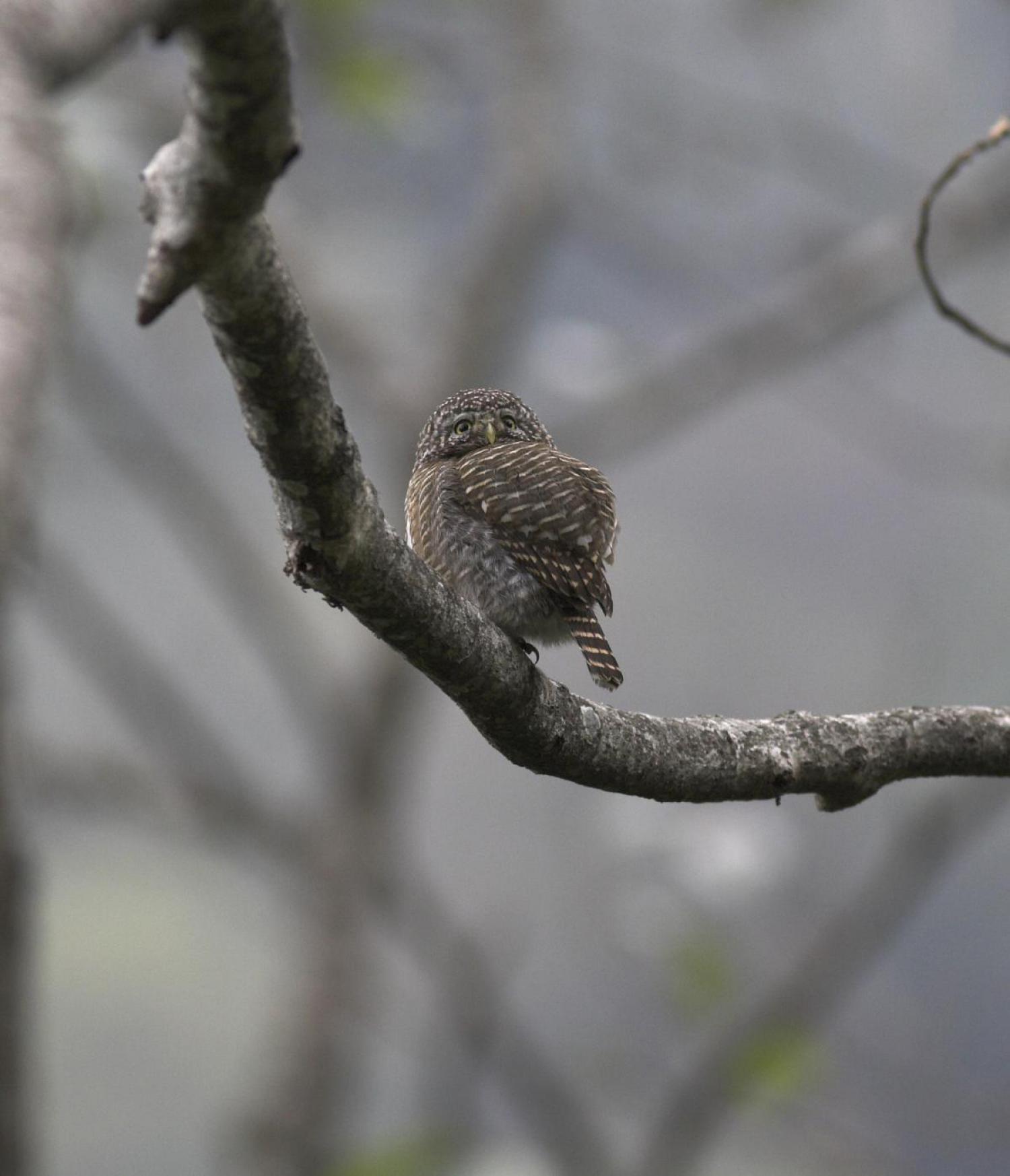
Collared owlets transition through various age-dependent colour morphs. A capture-recapture study of collared owlets in Taiwan provided evidence of this. On the first capture, the individual was 56 days old and showed fledgling colour morph stage; having less spots and barring on the back and top of the head and not having a completely formed occipital. On the second recapture, the individual was captured 165 days after hatching and demonstrated a rufous morph; having an overall orange-red colour, barred back, spots on the head and a formed occipital. On the third recapture, the individual was 394 days old and was in its final grey morph.
Vocalizations
The collared owlet has very unusual but distinctive vocalizations. The male produces a 4-note phrase "wüp-wüwü-wüp" repeated at intervals of a few seconds, sometimes having incomplete phrases ending in "wüwü". Their call starts mellow and becomes shriller with excitement while turning their head in all directions, creating a ventriloquial effect and making it hard to locate the bird.
Distribution and habitat
The collared owlet is a resident bird in its range.
Distribution
The collared owlet has a very large range occurring in the Himalayas of northern Pakistan all the way to eastern China and Taiwan. Its range extends southwards through Malaysia. This bird can be found in the following countries: Bhutan, Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, China, India, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, Taiwan, Thailand and Viet Nam.
Habitat
Their preferred habitat varies from evergreen forests, forest edges, mixed deciduous-evergreen forests with oak, rhododendron and fir and open woodlands with scrub. They can be found in submontane and montane habitats varying between 1350–2750 meters in altitude, but they have also been seen near cultivated lands as low as 700 meters in altitude.
Species in the genus Glaucidium are secondary cavity-nesters. For example, the Asian barred owlet was found to use the nest cavity of a collared scops owl once it was no longer using the nest. As for its other close relative, a study showed that the jungle owlet was found active in a secondary cavity nest in riparian forests. Just like the collared owlet's relatives, this small owl does not create its own nest, but rather nests in natural tree hollows or chambers created by woodpeckers and barbets.
Behaviour and ecology
Compared to other owls in the genus Glaucidium, the collared owlet is most active during daylight. Being diurnal, this bird can be seen perching, hunting and calling during most parts of the day, and sometimes during the night. It is often mobbed by other small birds when roosting.
Breeding
Although not much is known about the reproductive methods of the collared owlet, it is believed that the mating couple only remains together during the period of breeding season, which is from March to April.
As mentioned previously, they nest in natural tree hollows or holes created by woodpeckers or barbets, which are often very rotten and found high in tree trunks that are in a clearing or in an open area in the forest. The eggs are laid between late April and mid-June and their young are fledged from mid-June to early August. Clutch size varies between 3 and 5 hatchlings, and their eggs are round and white.
Food and feeding
Few studies has precisely identified the exact diet of the collared owlet, but we can presume that it is similar to the diet of its closest relative, the jungle owlet. The jungle owlet is seen to prey on small mammals such as house mice, little Indian field mice, brown spiny mice and white-toothed pygmy shrews; reptiles such as skinks; birds; amphibians and many invertebrates. Therefore, the diet of the collared owlet consists mainly on small birds, insect, lizards, invertebrates and small mammals. Although its small size, this raptor is extremely fierce and has been seen to capture prey as large as itself. Once their prey is captured, it is brought to a perch by its talons and torn up with upward pulls of the bill.
Status
Although the collared owlet is at least concern on the IUCN Red list, its main threat is habitat loss. In a study examining the effects of fragmentation on nocturnal birds in Asia, collared owlets were never found in forest fragments smaller than 100 hectares. The authors concluded that anthropogenic pressures such as deforestation can affect even small species such as the collared owlet.
This article uses material from Wikipedia released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike Licence 3.0. Eventual photos shown in this page may or may not be from Wikipedia, please see the license details for photos in photo by-lines.
Category / Seasonal Status
BCST Category: Recorded in an apparently wild state within the last 50 years
BCST Seasonal status: Resident or presumed resident
Scientific classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Strigiformes
- Family
- Strigidae
- Genus
- Glaucidium
- Species
- Glaucidium brodiei
Common names
- Thai: นกเค้าแคระ
Subspecies
Glaucidium brodiei borneense, Richard Bowdler Sharpe, 1893
Glaucidium brodiei brodiei, E. Burton, 1836
Glaucidium brodiei pardalotum, Robert Swinhoe, 1863
Glaucidium brodiei sylvaticum, Charles Lucien Bonaparte, 1850
Conservation status

Least Concern (IUCN3.1)
Photos
Please help us review the bird photos if wrong ones are used. We can be reached via our contact us page.
Range Map
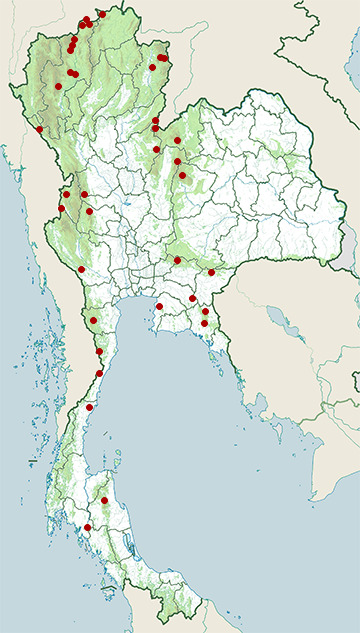
- Chiang Dao District, Chiang Mai
- Chiang Dao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Doi Inthanon National Park
- Doi Lang
- Doi Pha Hom Pok National Park
- Doi Phu Kha National Park
- Doi Suthep - Pui National Park
- Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary
- Huai Yang Waterfall National Park
- Kaeng Krachan National Park
- Khao Ang Rue Nai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Khao Khiao - Khao Chomphu Wildlife Sanctuary
- Khao Khitchakut National Park
- Khao Luang National Park
- Khao Phra - Bang Khram Wildlife Sanctuary
- Khao Soi Dao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Khao Yai National Park
- Khun Nan National Park
- Kui Buri National Park
- Mae Ai District, Chiang Mai
- Mae Fa Luang District, Chiang Rai
- Mae Moei National Park
- Mae Wong National Park
- Mueang Chiang Mai District, Chiang Mai
- Nam Nao National Park
- Pang Sida National Park
- Pathio District, Chumphon
- Pha Daeng National Park
- Phu Hin Rong Kla National Park
- Phu Khiao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Phu Luang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Phu Soi Dao National Park
- Phu Suan Sai National Park
- Sai Yok District, Kanchanaburi
- Tham Sakoen National Park
- Thung Yai Naresuan Wildlife Sanctuary
- Umphang Wildlife Sanctuary


