Species of Thailand
Collared kingfisher
Todiramphus chloris
Pieter Boddaert, 1783
In Thai: นกกินเปี้ยว
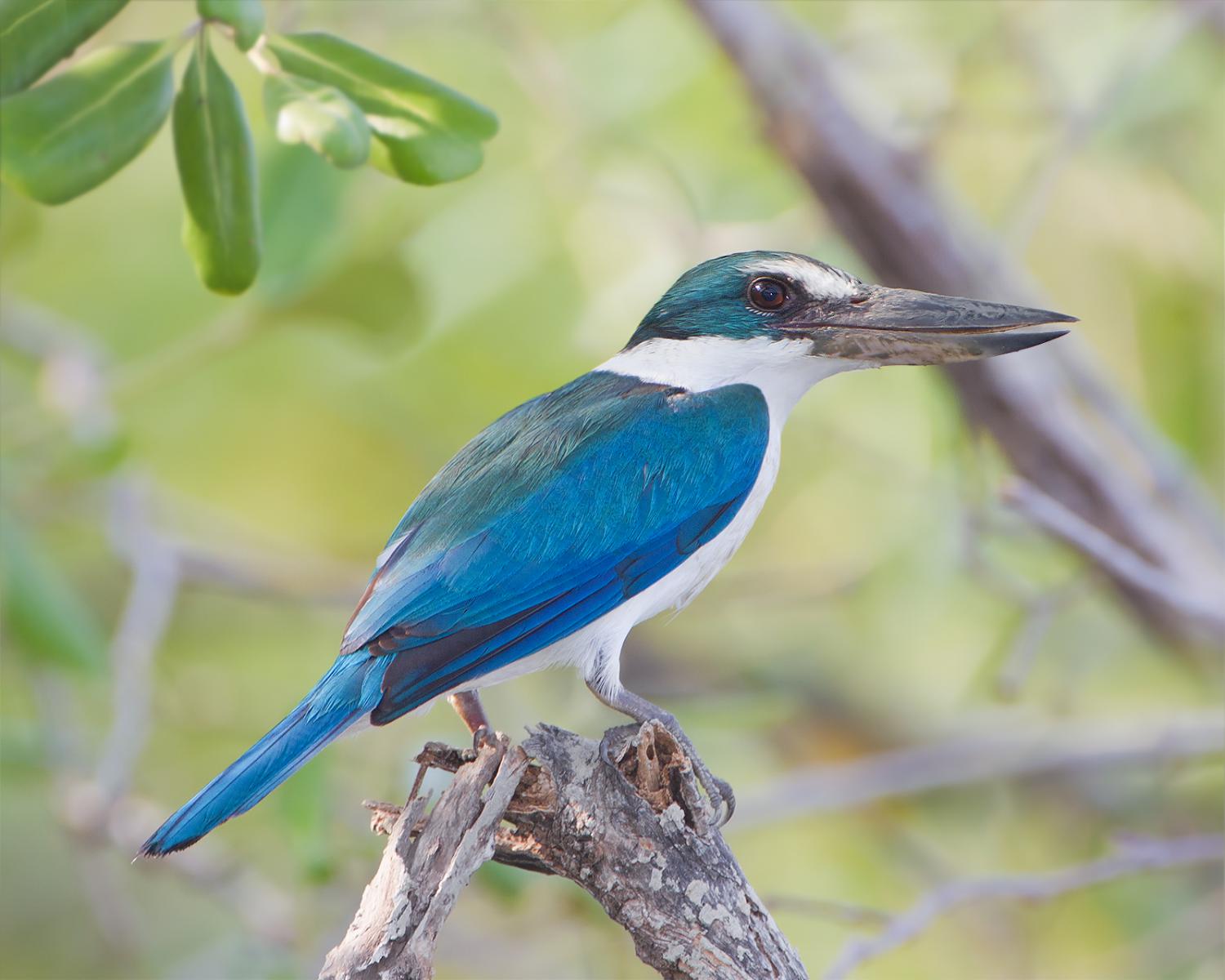
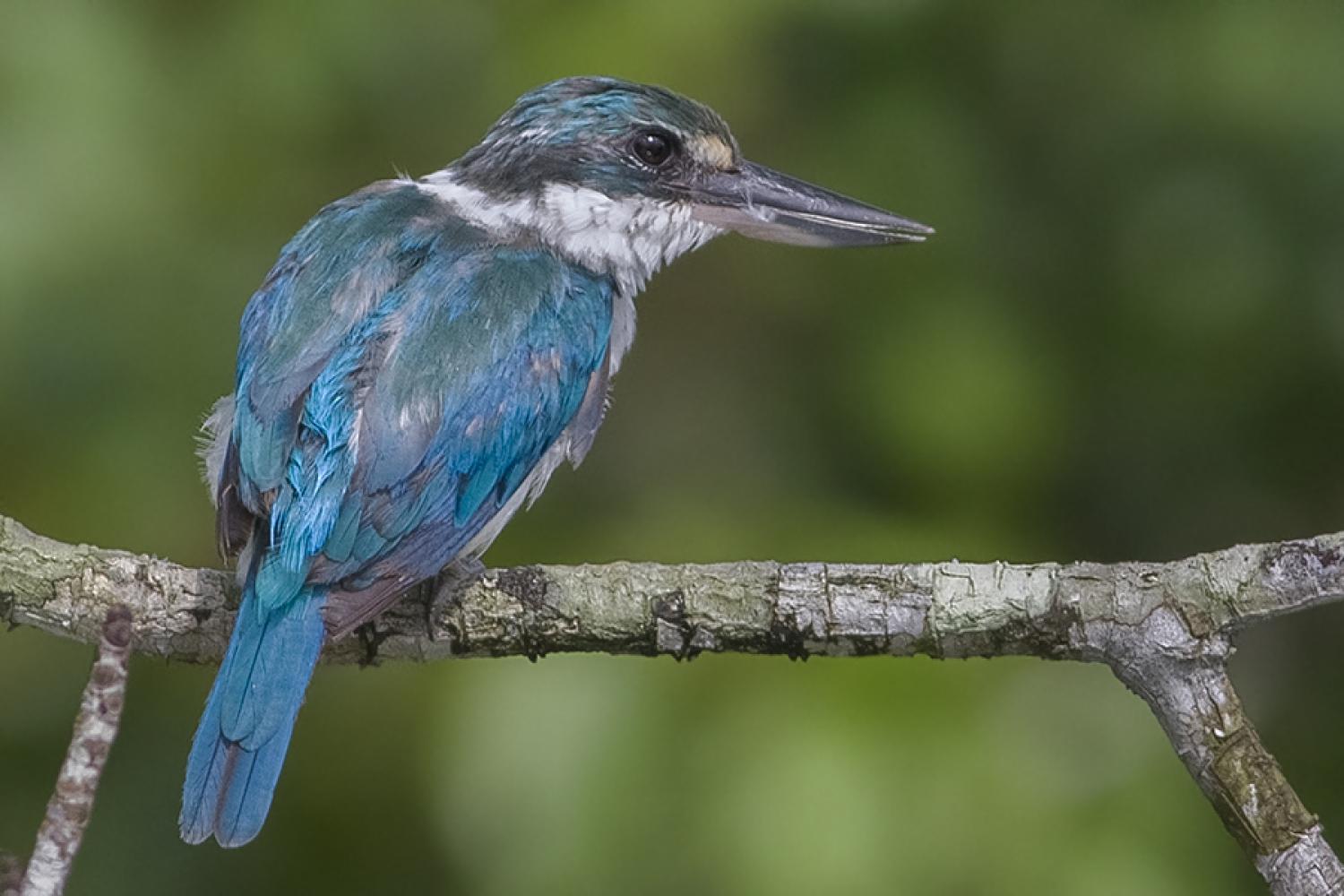
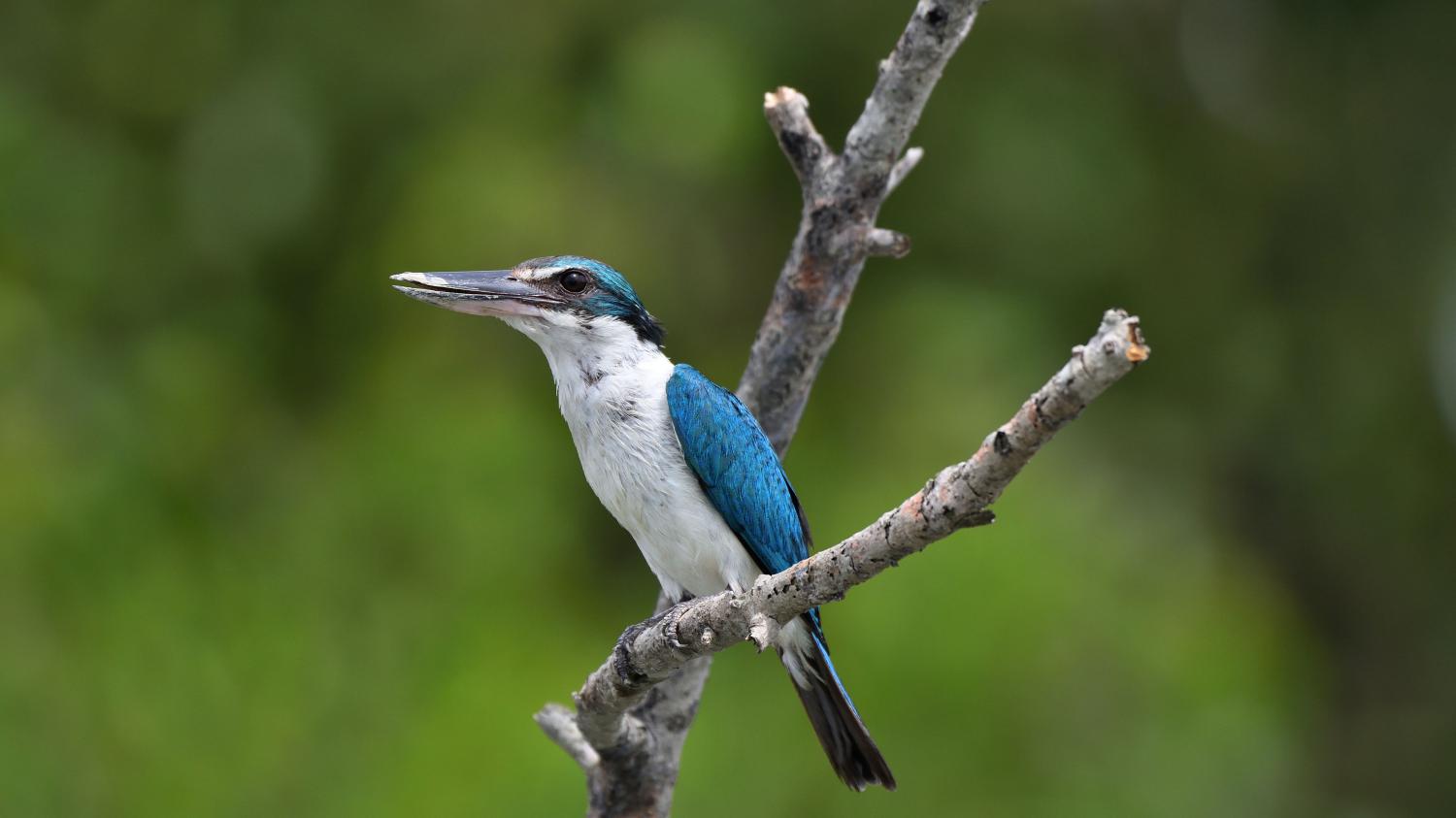
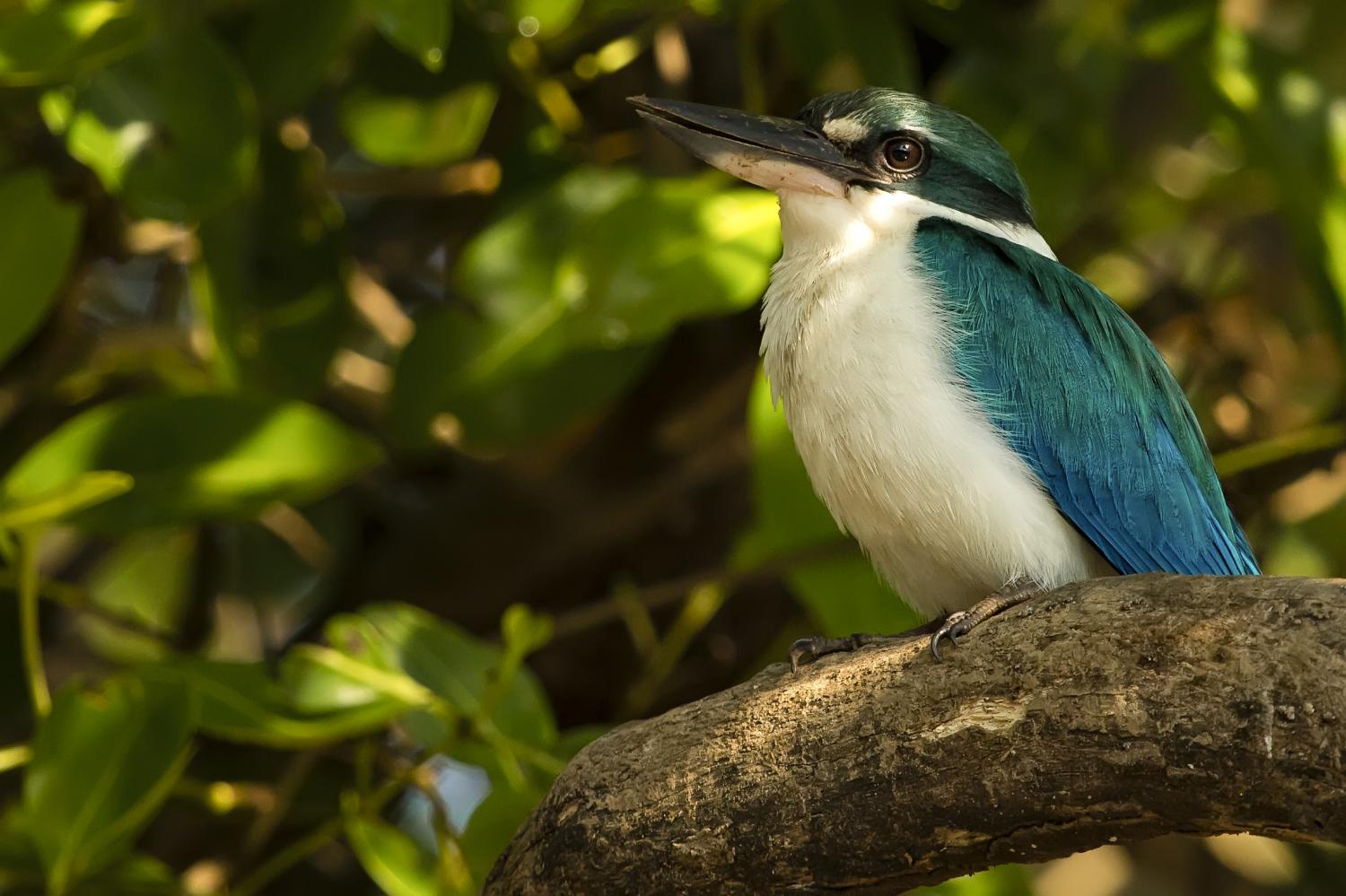
The collared kingfisher (Todiramphus chloris) is a medium-sized kingfisher belonging to the subfamily Halcyoninae, the tree kingfishers. It is also known as the white-collared kingfisher or mangrove kingfisher. It has a wide range extending from the Red Sea across southern Asia to Polynesia. A number of subspecies and subspecies groups have been split from this species including the Pacific kingfisher, the islet kingfisher, the Torresian kingfisher, the Mariana kingfisher, and the Melanesian kingfisher.
Taxonomy
The collared kingfisher was described by the French polymath Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon in his Histoire Naturelle des Oiseaux in 1780. The bird was also illustrated in a hand-coloured plate engraved by François-Nicolas Martinet in the Planches Enluminées D'Histoire Naturelle. This was produced under the supervision of Edme-Louis Daubenton to accompany Buffon's text. Neither the plate caption nor Buffon's description included a scientific name but in 1783 the Dutch naturalist Pieter Boddaert coined the binomial name Alcedo chloris in his catalogue of the Planches Enluminées. The type locality is the island of Buru within Indonesia. The current genus Todiramphus was introduced by the French surgeon and naturalist René Lesson in 1827. The specific epithet chloris is modern Latin for 'green' or 'greenish'.
List of subspecies
There are numerous subspecies in the species’ largely coastal and insular range from the Red Sea to Polynesia:
Red Sea and Arabian coasts
- T. c. abyssinicus (Pelzeln, 1856) – southern Red Sea coasts of Somalia and Arabia
- T. c. kalbaensis (Cowles, 1980) – coasts of northeastern United Arab Emirates (Khawr Kalba) and northern Oman
India and Indian Ocean
- T. c. vidali (Sharpe, 1892) – western India from Ratnagiri to Kerala.
- T. c. davisoni (Sharpe, 1892) – Andaman Islands and Coco Islands (in Bay of Bengal, south of Myanmar)
- T. c. occipitalis (Blyth, 1846) – Nicobar Islands
South East Asia
- T. c. humii (Sharpe, 1892) – coasts of West Bengal eastwards to Burma (including the Mergui Archipelago), the Malay Peninsula, Tioman and north-eastern Sumatra.
- T. c. armstrongi (Sharpe, 1892) – interior of Burma and Thailand, Indochina and eastern China
- T. c. laubmannianus (Grote, 1933) – Sumatra (excluding northeast) and Borneo, including intervening islands.
- T. c. chloropterus (Oberholser, 1919) – islands off western Sumatra
- T. c. azelus (Oberholser, 1919) – Enggano (off southwestern Sumatra)
- T. c. palmeri (Oberholser, 1919) – Java, Bali, Bawean and Kangean Islands
- T. c. collaris (Scopoli, 1786) – Philippines, including Palawan and nearby islands.
Wallacea, New Guinea
- T. c. chloris (Boddaert, 1783) – Talaud and Sangihe Islands through Sulawesi to the Lesser Sundas (east from Lombok), West Papuan Islands and north-western New Guinea (Vogelkop and Onin peninsulas).
Micronesia
- T. c. teraokai (Nagamichi Kuroda, 1915) – Palau
Description
The collared kingfisher is 23 to 25 cm long and the male weighs 51 to 90 g, while the female weighs 54-100 g. It varies from blue to green above while the underparts can be white or buff. There is a white collar around the neck, giving the bird its name. Some races have a white or buff stripe over the eye while others have a white spot between the eye and bill. There may be a black stripe through the eye. The large bill is black with a pale yellow base to the lower mandible. Females tend to be greener than the males. Immature birds are duller than the adults with dark scaly markings on the neck and breast.
It has a variety of calls which vary geographically. The most typical call is a loud, harsh and metallic "kee-kee-kee" repeated several times.
Distribution and habitat
It is most commonly found in coastal areas, particularly in mangrove swamps. It also inhabits farmland, open woodland, grassland and gardens. In some parts of its range, especially on islands, it can be seen further inland, ranging into forest or into mountain areas. Birds often perch conspicuously on wires, rocks or bare branches.
The subspecies that occurs furthest west in the Eurasian/African landmass is T. c. abyssinica of north-east Africa, which is found in patches of mangroves in Eritrea and has also been recorded from Sudan and Somalia. Further east in Arabia is the endangered race T. c. kalbaensis with a population of 55 pairs or fewer; these are almost entirely restricted to Khor Kalba in the United Arab Emirates, but breeding has also occurred recently at Khor Shinas in Oman. Further subspecies occur locally around the coasts of India and Bangladesh and on the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. In Southeast Asia and Indonesia the species is widespread and common, occurring far inland in some regions.
Feeding
Small crabs and shrimps are the favoured food in coastal regions but a wide variety of other animals are eaten including insects (including beetles, cicadas, stick-insects, grasshoppers, moths and butterflies), spiders, earthworms, snails, frogs, lizards, small snakes, small fish, and sometimes small and mice. The collared kingfisher perches almost motionless for long periods waiting for prey. When it spots something it glides down to catch it and then flies back to the perch where larger items are pounded against the branch to subdue them. Any indigestible remains are regurgitated as pellets.
Reproduction
The nest is a hole, either a natural tree hole or a burrow excavated by the birds themselves in a rotten tree, arboreal termite nest or earth bank. They will also occupy old woodpecker holes. A clutch of usually two to five rounded, whitish eggs are laid directly on the floor of the burrow with no nest material used. Both parents take part in incubating the eggs and feeding the chicks. The young birds leave the nest about 44 days after hatching. Two broods are often raised in a year.
Conservation status
With a very wide distribution and common to abundant population, the collared kingfisher is classed as least concern on the IUCN Red List.
This article uses material from Wikipedia released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike Licence 3.0. Eventual photos shown in this page may or may not be from Wikipedia, please see the license details for photos in photo by-lines.
Category / Seasonal Status
BCST Category: Recorded in an apparently wild state within the last 50 years
BCST Seasonal status: Resident or presumed resident
Scientific classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Coraciiformes
- Family
- Alcedinidae
- Genus
- Todiramphus
- Species
- Todiramphus chloris
Common names
- Thai: นกกินเปี้ยว
Subspecies
Todiramphus chloris abyssinicus, August von Pelzeln, 1856
Range: Southern Red Sea coasts of Somalia and Arabia
Todiramphus chloris alberti, Lionel Walter Rothschild & Ernst Johann Otto Hartert, 1905
Range: Western and central Solomon Islands
Todiramphus chloris albicilla, Charles Henri Frédéric Dumont de Sainte-Croix, 1823
Range: Saipan and Tinian
Todiramphus chloris amoenus, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1931
Range: Rennell and Bellona
Todiramphus chloris armstrongi, Richard Bowdler Sharpe, 1892
Range: Interior of Burma and Thailand, Indochina and eastern China
Todiramphus chloris azelus, Harry Church Oberholser, 1919
Range: Enggano
Todiramphus chloris bennetti, Sidney Dillon Ripley, 1947
Range: Nissan Island
Todiramphus chloris brachyurus, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1931
Range: Reef Islands
Todiramphus chloris chloris, Pieter Boddaert, 1783
Range: Talaud and Sangihe Islands through Sulawesi to the Lesser Sundas, West Papuan Islands and north-western New Guinea
Todiramphus chloris chloropterus, Harry Church Oberholser, 1919
Range: Islands off western Sumatra
Todiramphus chloris collaris, Giovanni Antonio Scopoli, 1786
Range: Philippines
Todiramphus chloris colonus, Ernst Johann Otto Hartert, 1896
Range: Louisiade Archipelago
Todiramphus chloris davisoni, Richard Bowdler Sharpe, 1892
Range: Andaman Islands
Todiramphus chloris erromangae, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1938
Range: Erromango and Anatom
Todiramphus chloris eximius, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1941
Range: Kadavu
Todiramphus chloris humii, Richard Bowdler Sharpe, 1892
Range: Coasts of West Bengal eastwards to Burma (including the Mergui Archipelago), the Malay Peninsula, Tioman and north-eastern Sumatra
Todiramphus chloris juliae, Ferdinand Heine, 1860
Range: Aoba and Maewo southwards to Efate
Todiramphus chloris kalbaensis, Cowles, 1980
Range: South Arabian coast
Todiramphus chloris laubmannianus, Hermann Grote, 1933
Range: Sumatra and Borneo, including intervening islands
Todiramphus chloris mala, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1935
Range: Malaita
Todiramphus chloris manuae, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1941
Range: Ofu-Olosega and Tau
Todiramphus chloris marinus, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1941
Range: Lau Archipelago
Todiramphus chloris matthiae, Oskar Heinroth, 1902
Range: St Matthias Islands
Todiramphus chloris melanodera, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1931
Range: Vanikoro
Todiramphus chloris novaehiberniae, Ernst Johann Otto Hartert, 1925
Range: South-west New Ireland
Todiramphus chloris nusae, Oskar Heinroth, 1902
Range: New Hanover, New Ireland and the Feni Islands
Todiramphus chloris occipitalis, Edward Blyth, 1846
Range: Nicobar Islands
Todiramphus chloris orii, Takatsukasa & Yamashina, 1931
Range: Rota
Todiramphus chloris ornatus, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1931
Range: Nendo and Tinakula
Todiramphus chloris owstoni, Lionel Walter Rothschild, 1904
Range: Asuncion, Agrihan, Pagan and Alamagan
Todiramphus chloris palmeri, Harry Church Oberholser, 1919
Range: Java, Bali, Bawean and Kangean Islands
Todiramphus chloris pavuvu, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1935
Range: Pavuvu
Todiramphus chloris pealei, Friedrich Hermann Otto Finsch & Gustav Hartlaub, 1867
Range: Tutuila
Todiramphus chloris pilbara, Ronals E. Johnstone, 1983
Range: Coastal north-western Australia: from the De Grey River to Exmouth Gulf
Todiramphus chloris regina, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1941
Range: Futuna
Todiramphus chloris sacer, Johann Friedrich Gmelin, 1788
Range: Central and southern Tonga. Gmelin originally named it Alcedo sacra. It was supposedly venerated by the locals, like the sacred kingfisher.
Todiramphus chloris santoensis, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1931
Range: Banks Islands southwards to Espiritu Santo and Malo
Todiramphus chloris solomonis, Edward Pierson Ramsay, 1882
Range: Makira and adjacent islands
Todiramphus chloris sordidus, John Gould, 1842
Range: Aru Islands, and northern and north-eastern coasts of Australia
Todiramphus chloris sororum, I. C. J. Galbraith & E. H. Galbraith, 1962
Range: Malaupaina and Malaulalo
Todiramphus chloris stresemanni, Alfred Louis Laubmann, 1923
Range: Islands between mainland New Guinea and New Britain
Todiramphus chloris tannensis, Richard Bowdler Sharpe, 1892
Range: Tanna
Todiramphus chloris teraokai, Nagamichi Kuroda, 1915
Range: Palau
Todiramphus chloris torresianus, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1931
Range: Hiw and Lo
Todiramphus chloris tristrami, Edgar Leopold Layard, 1880
Range: New Britain
Todiramphus chloris utupuae, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1931
Range: Utupua
Todiramphus chloris vicina, Ernst Walter Mayr, 1931
Range: Duff Islands
Todiramphus chloris vidali, Richard Bowdler Sharpe, 1892
Range: Western India from Ratnagiri to Kerala
Todiramphus chloris vitiensis, Titian Ramsay Peale, 1848
Range: Vanua Levu, Taveuni, Viti Levu, Koro, Ovalau and Gau
Synonyms
- Todirhamphus chloris
- Halcyon chloris
Conservation status

Least Concern (IUCN3.1)
Photos
Please help us review the bird photos if wrong ones are used. We can be reached via our contact us page.
Range Map
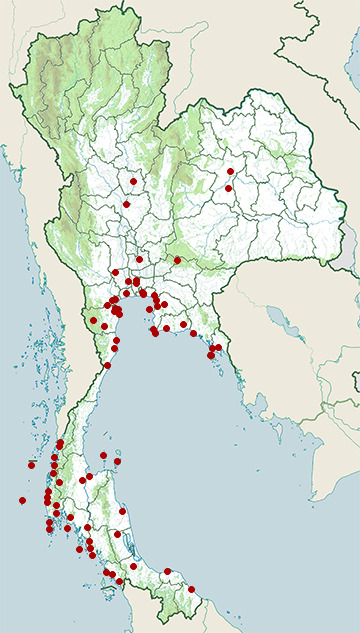
- Amphawa District, Samut Songkhram
- Ang Thong National Marine Park
- Ao Manao-Khao Tanyong National Park
- Ao Phang-Nga National Park
- Ban Bueng District, Chonburi
- Ban Laem District, Phetchaburi
- Ban Phai District, Khon Kaen
- Bang Pakong District, Chachoengsao
- Bang Phra Non-Hunting Area
- Bang Pu Recreation Centre
- Bangkok Province
- Bueng Boraped Non-Hunting Area
- Hat Chao Mai National Park
- Hat Yai District, Songkhla
- Kaeng Krachan National Park
- Kamphaeng Saen District, Nakhon Pathom
- Khao Lak - Lam Ru National Park
- Khao Phra - Bang Khram Wildlife Sanctuary
- Khao Sam Roi Yot National Park
- Khao Sok National Park
- Khao Yai National Park
- Khao Yoi District, Phetchaburi
- Khuan Khanun District, Phatthalung
- Khung Kraben Non-Hunting Area
- Khura Buri District, Phang Nga
- Klaeng District, Rayong
- Ko Chang District, Trat
- Ko Chang National Park
- Ko Lanta National Park
- Ko Libong
- Ko Samui District, Surat Thani
- Ko Sichang District, Chonburi
- Laem Ngop District, Trat
- Laem Pak Bia
- Laem Son National Park
- Mu Ko Phetra National Park
- Mu Ko Ranong National Park
- Mueang Chonburi District, Chonburi
- Mueang Khon Kaen District, Khon Kaen
- Mueang Krabi District, Krabi
- Mueang Nonthaburi District, Nonthaburi
- Mueang Pattani District, Pattani
- Mueang Phang Nga District, Phang Nga
- Mueang Phetchaburi District, Phetchaburi
- Mueang Phuket District, Phuket
- Mueang Prachuap Khiri Khan District, Prachuap Khiri Khan
- Mueang Ranong District, Ranong
- Mueang Rayong District, Rayong
- Mueang Samut Prakan District, Samut Prakan
- Mueang Samut Sakhon District, Samut Sakhon
- Mueang Samut Songkhram District, Samut Songkhram
- Mueang Satun District, Satun
- Mueang Surat Thani District, Surat Thani
- Mueang Trat District, Trat
- Pak Phanang District, Nakhon Si Thammarat
- Pak Thale
- Phi Phi Islands
- Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya District, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya
- Phunphin District, Surat Thani
- Phutthamonthon District, Nakhon Pathom
- Pran Buri Forest Park
- Samae San Island
- Samut Prakan Province
- Sattahip District, Chonburi
- Sikao District, Trang
- Similan Islands
- Suk Samran District, Ranong
- Surin Islands
- Takua Pa District, Phang Nga
- Taphan Hin District, Phichit
- Tha Phae District, Satun
- Tha Yang District, Phetchaburi
- Thai Mueang District, Phang Nga
- Thalang District, Phuket



