Species of Thailand
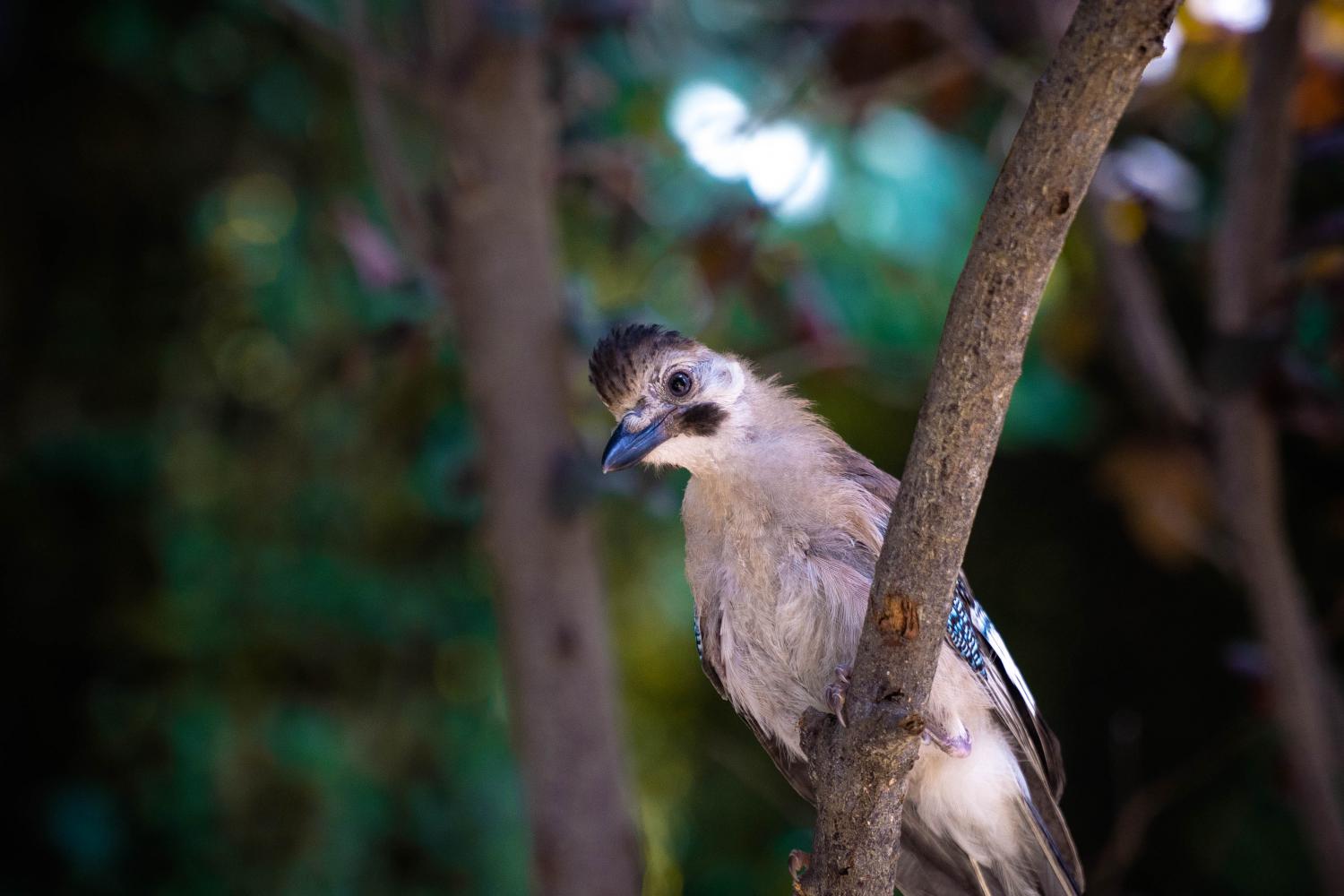
White-faced jay
Garrulus leucotis
Carolus Linnaeus, 1758
In Thai: นกปีกลายสก๊อต
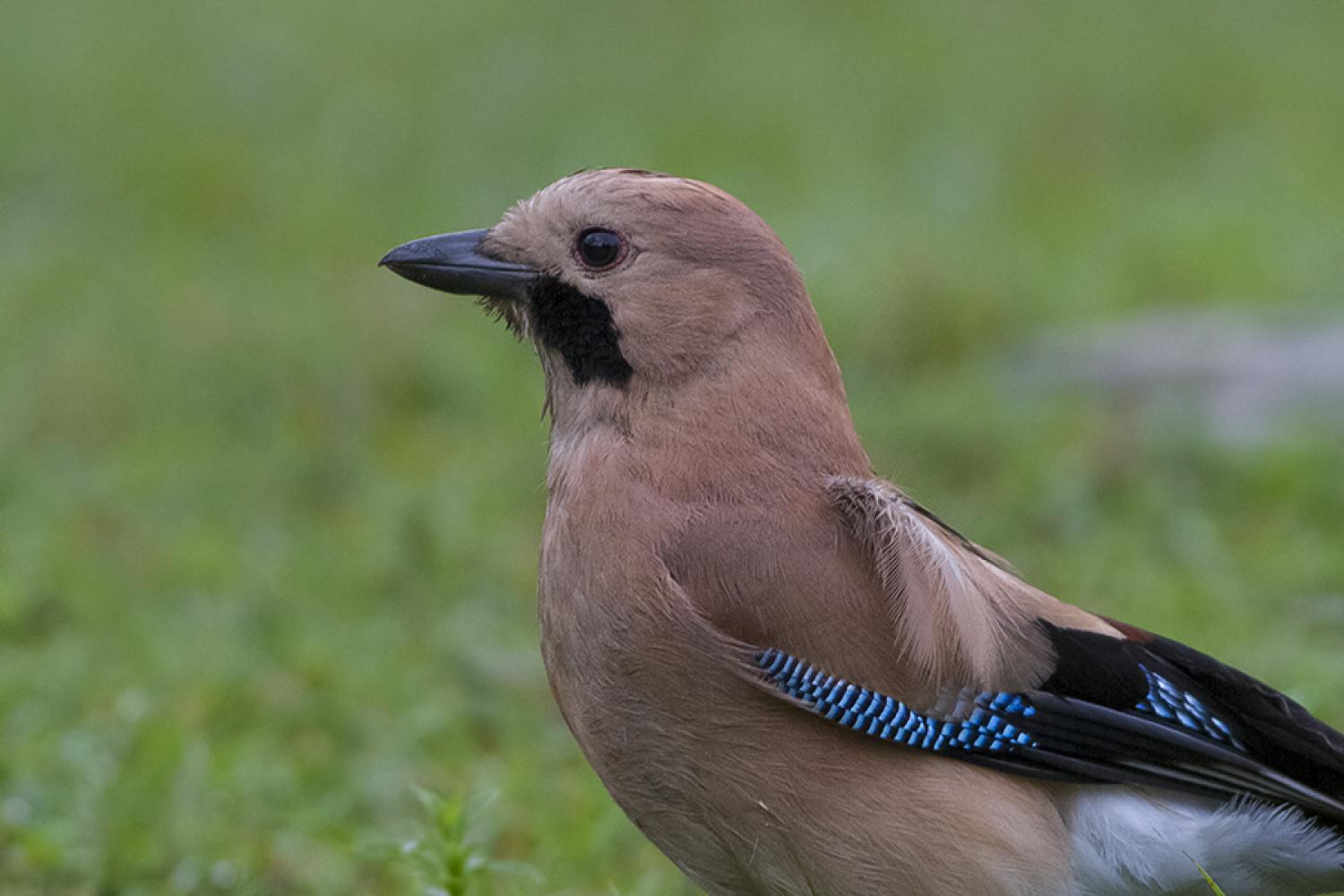
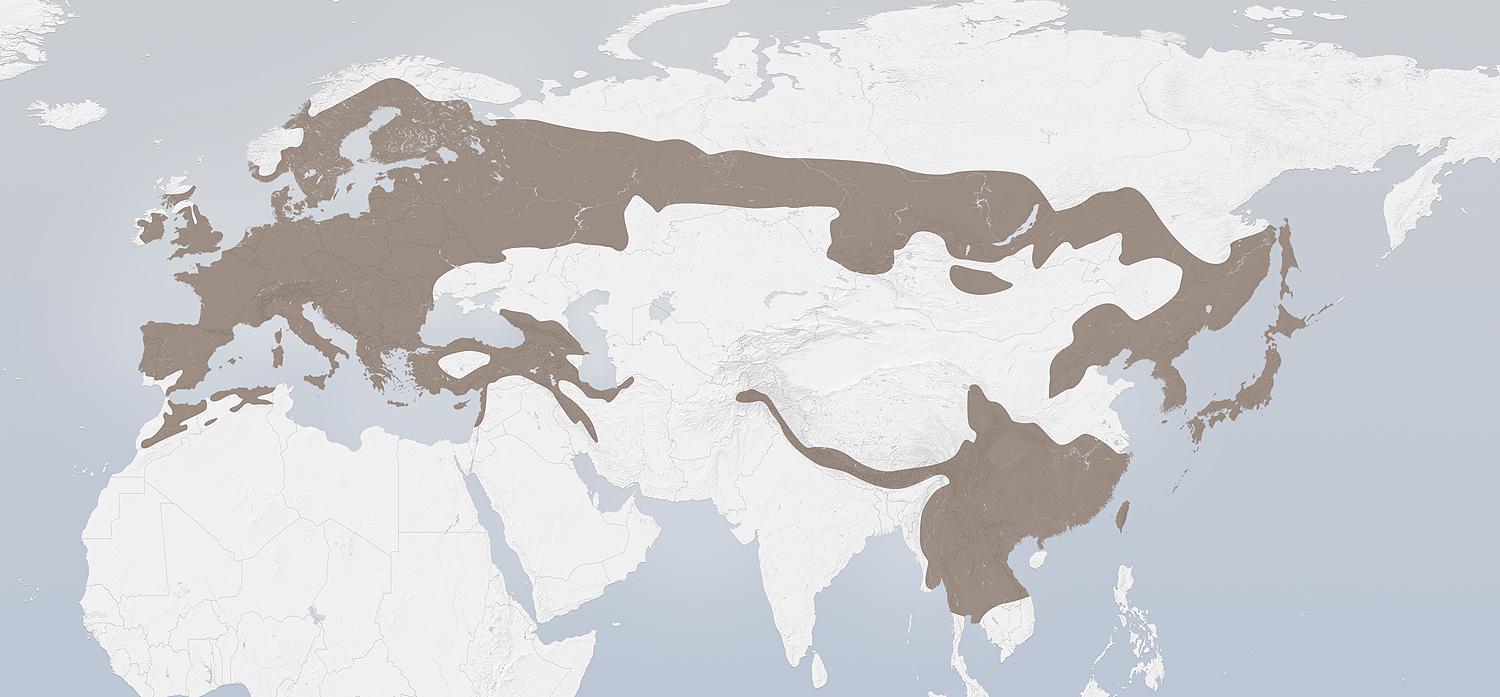
The Eurasian jay (Garrulus glandarius) is a species of bird occurring over a vast region from western Europe and north-west Africa to the Indian subcontinent and further to the eastern seaboard of Asia and down into south-east Asia. Across its vast range, several very distinct racial forms have evolved to look very different from each other, especially when forms at the extremes of its range are compared.
The bird is called jay, without any epithets, by English speakers in Great Britain and Ireland.
Taxonomy and systematics
The Eurasian jay was one of the many species originally described by Carl Linnaeus in his landmark 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. He recognised its affinity with other corvids, naming it Corvus glandarius. The current scientific name is from Latin; garrulus means noisy or chattering, and glandarius is "of acorns", a favoured food.
Eight racial groups (33 subspecies in total) are recognised by Madge & Burn (1994): Jena Phyletic Museum, in Germany, features an excellent display of plumage variations across these races, which is used as a particularly striking example of the variation that can be found within species.
- the nominate group (nine European races), with a streaked crown.
- the cervicalis group (three races in North Africa), with a rufous nape, grey mantle, very pale head sides, and a streaked or black crown.
- the atricapillus group (four races in Middle East, Crimea & Turkey), with a uniform mantle & nape, black crown and very pale face.
- the race hyrcanus (Caspian Hyrcanian mixed forests of Iran), small with black forecrown and broadly streaked hindcrown.
- the brandtii group (four races in Siberia and northern Japan), with a streaked crown, reddish head, dark iris and grey mantle.
- the leucotis group (two races in south-east Asia), with no white in the wing, a white forecrown, black hindcrown and much white on the sides of the head.
- the bispecularis group (six races in the Himalayan region), with an unstreaked rufous crown, and no white wing-patch.
- the japonicus group (four races in the southern Japanese islands), with a large white wing-patch, blackish face and scaled crown.
Distribution and habitat
A member of the widespread jay group, and about the size of the jackdaw, it inhabits mixed woodland, particularly with oaks, and is a habitual acorn hoarder. In recent years, the bird has begun to migrate into urban areas, possibly as a result of continued erosion of its woodland habitat. Before humans began planting the trees commercially on a wide scale, Eurasian jays were the main source of movement and propagation for the European oak (Q. robur), each bird having the ability to spread more than a thousand acorns each year. Eurasian jays will also bury the acorns of other oak species, and have been cited by the National Trust as a major propagator of the largest population of holm oak (Q. ilex) in Northern Europe, situated in Ventnor on the Isle of Wight. Jays have been recorded carrying single acorns as far as 20 km, and are credited with the rapid northward spread of oaks following the last ice age.
Behaviour and ecology
Its usual call is the alarm call which is a harsh, rasping screech and is used upon sighting various predatory animals, but the jay is well known for its mimicry, often sounding so like a different species that it is virtually impossible to distinguish its true identity unless the jay is seen. It will even imitate the sound of the bird it is attacking, such as a tawny owl, which it does if attacking during the day. However, the jay is a potential prey item for owls at night and other birds of prey such as goshawks and peregrines during the day.
Diet
Feeding in both trees and on the ground, it takes a wide range of invertebrates including many pest insects, acorns (oak seeds, which it buries for use during winter), beech and other seeds, fruits such as blackberries and rowan berries, young birds and eggs, bats, and small rodents. Like most species, the jay's diet changes with the seasons but is noteworthy for its prolific caching of food—especially oak acorns and beechnuts—for winter and spring. While caching occurs throughout the year, it is most intense in the autumn.
Breeding
It nests in trees or large shrubs laying usually 4–6 eggs that hatch after 16–19 days and are fledged generally after 21–23 days. Both sexes typically feed the young.
Health
For more information, see Anting (bird activity)
In order to keep its plumage free from parasites, it lies on top of anthills with spread wings and lets its feathers be sprayed with formic acid.
Intelligence
Similar to other corvids, Eurasian jays have been reported to plan for future needs. Male Eurasian jays also take into account the desires of their partner when sharing food with her as a courtship ritual and when protecting food items from stealing conspecifics.
This article uses material from Wikipedia released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike Licence 3.0. Eventual photos shown in this page may or may not be from Wikipedia, please see the license details for photos in photo by-lines.
Category / Seasonal Status
BCST Category: Recorded in an apparently wild state within the last 50 years
BCST Seasonal status: Resident or presumed resident
Scientific classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Passeriformes
- Family
- Corvidae
- Genus
- Garrulus
- Species
- Garrulus leucotis
Common names
- Thai: นกปีกลายสก๊อต
Conservation status

Least Concern (IUCN3.1)
Photos
Please help us review the bird photos if wrong ones are used. We can be reached via our contact us page.
Range Map
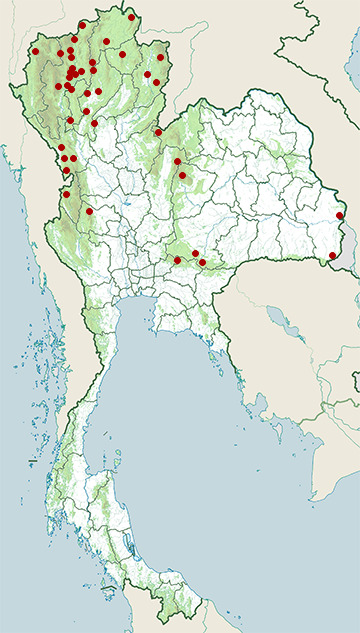
- Chae Son National Park
- Chiang Dao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Chiang Khong District, Chiang Rai
- Doi Chong National Park
- Doi Inthanon National Park
- Doi Lo District, Chiang Mai
- Doi Pha Hom Pok National Park
- Doi Phu Kha National Park
- Doi Saket District, Chiang Mai
- Doi Suthep - Pui National Park
- Hang Chat District, Lampang
- Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary
- Huai Nam Dang National Park
- Khao Yai National Park
- Khun Chae National Park
- Khun Phawo National Park
- Mae Charim National Park
- Mae Ping National Park
- Mae Rim District, Chiang Mai
- Mae Sot District, Tak
- Mae Taeng District, Chiang Mai
- Mueang Chiang Mai District, Chiang Mai
- Mueang Lampang District, Lampang
- Mueang Nan District, Nan
- Na Haeo District, Loei
- Nam Nao National Park
- Namtok Mae Surin National Park
- Namtok Pha Charoen National Park
- Op Khan National Park
- Pa Sang District, Lamphun
- Pha Daeng National Park
- Pha Taem National Park
- Phan District, Chiang Rai
- Phu Chong Na Yoi National Park
- Phu Khiao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Sakaerat Environmental Research Station
- Si Satchanalai National Park
- Taksin Maharat National Park
- Thap Lan National Park
- Umphang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Wiang Lo Wildlife Sanctuary