Species of Thailand
Cave racer
Elaphe taeniura
Edward Drinker Cope, 1861
In Thai: งูกาบหมากถ้ำ, ngu gaap maag tham
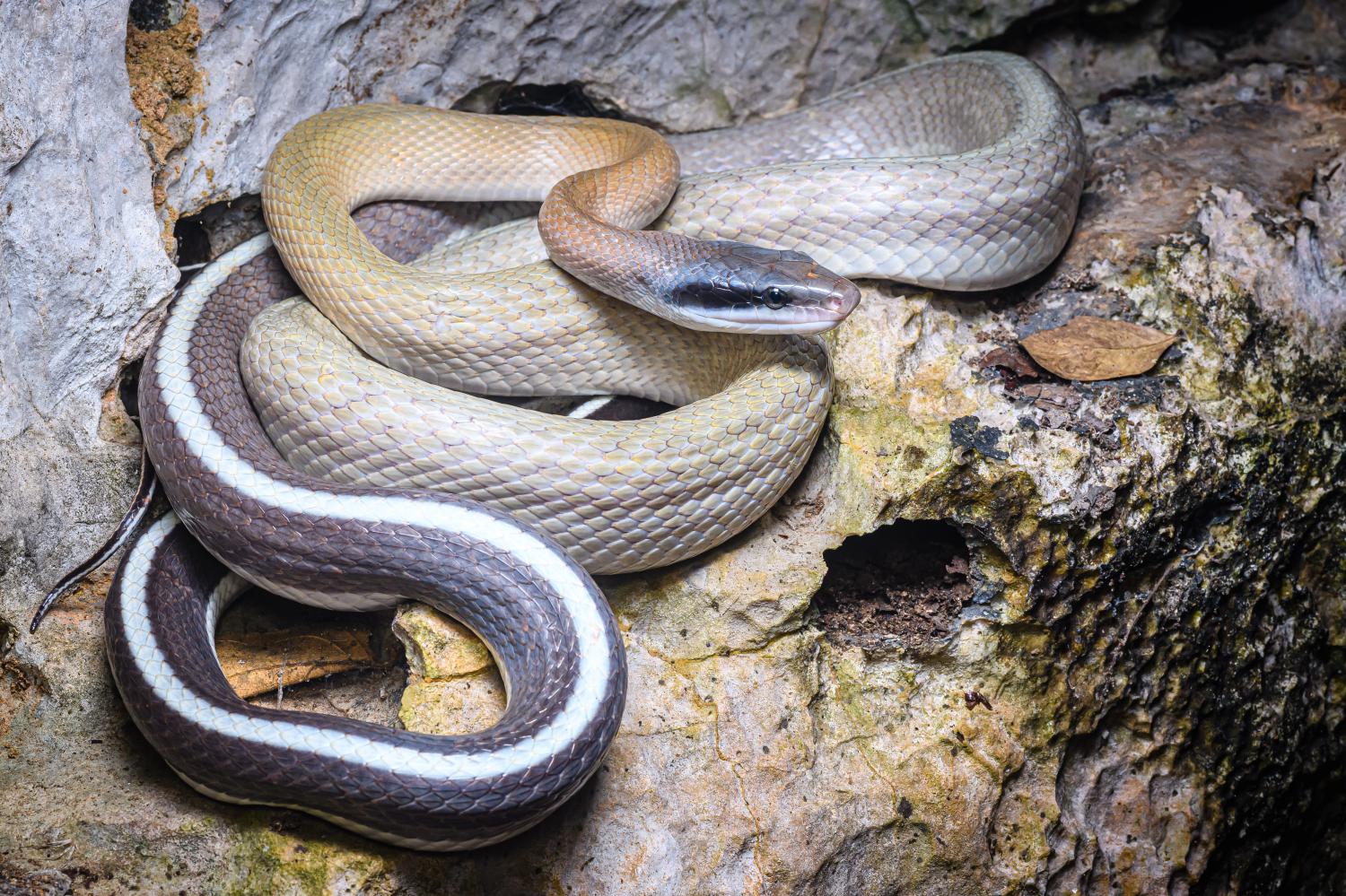
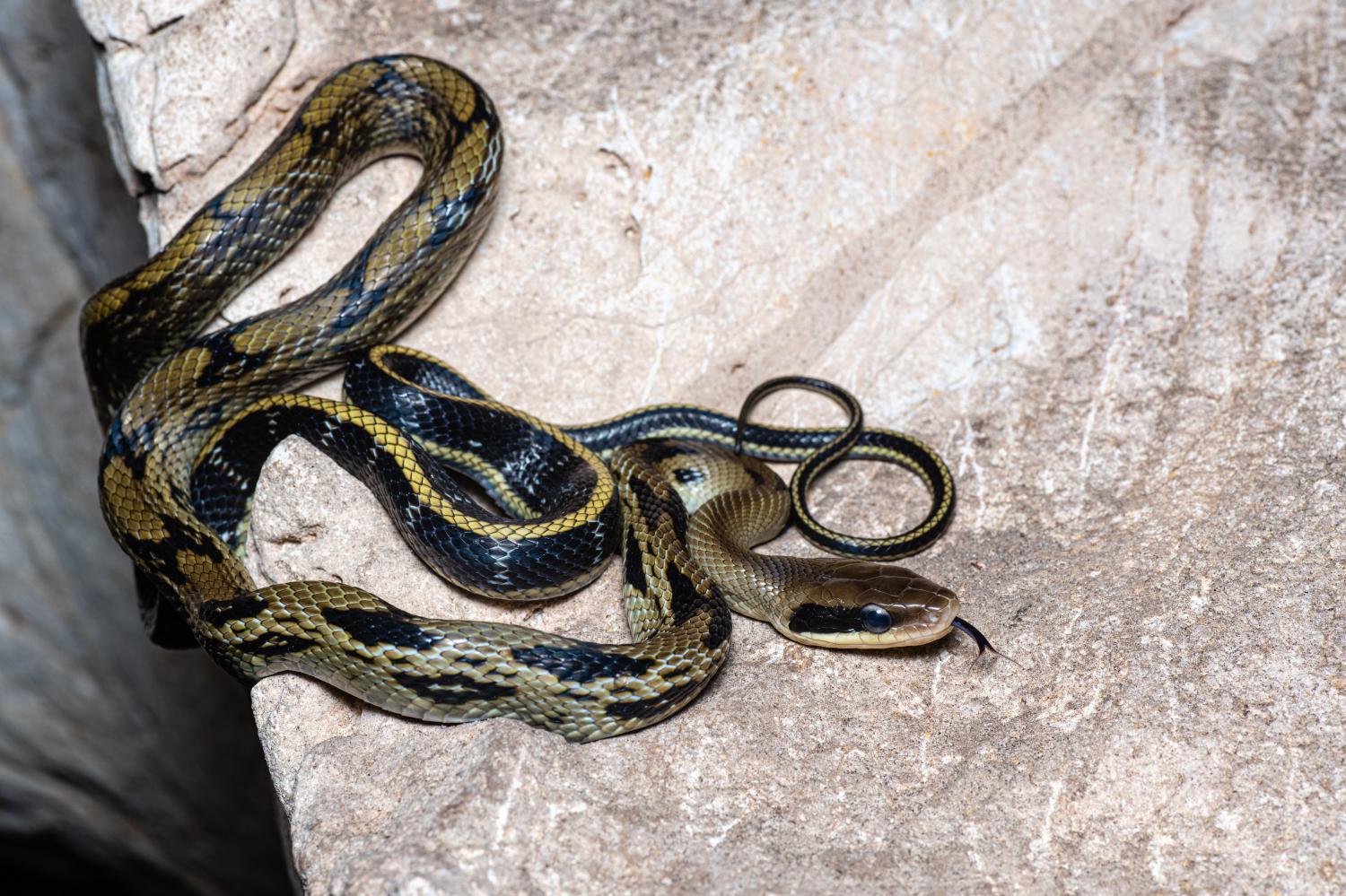
The beauty rat snake (Elaphe taeniura), also called the beauty ratsnake, the beauty snake, or the cave racer, is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. The species is native to the eastern and southeastern regions of Asia. It is a long, thin, semi-arboreal species of snake with several recognized subspecies. This constrictor feeds on rodents, and though it is favored in some locations as a natural pest control or pet, it is also considered an invasive species in other locations.
Description
Living about 15–25 years, the average length of the beauty rat snake (including the tail) is about 1.2–1.8 m.
Coloration
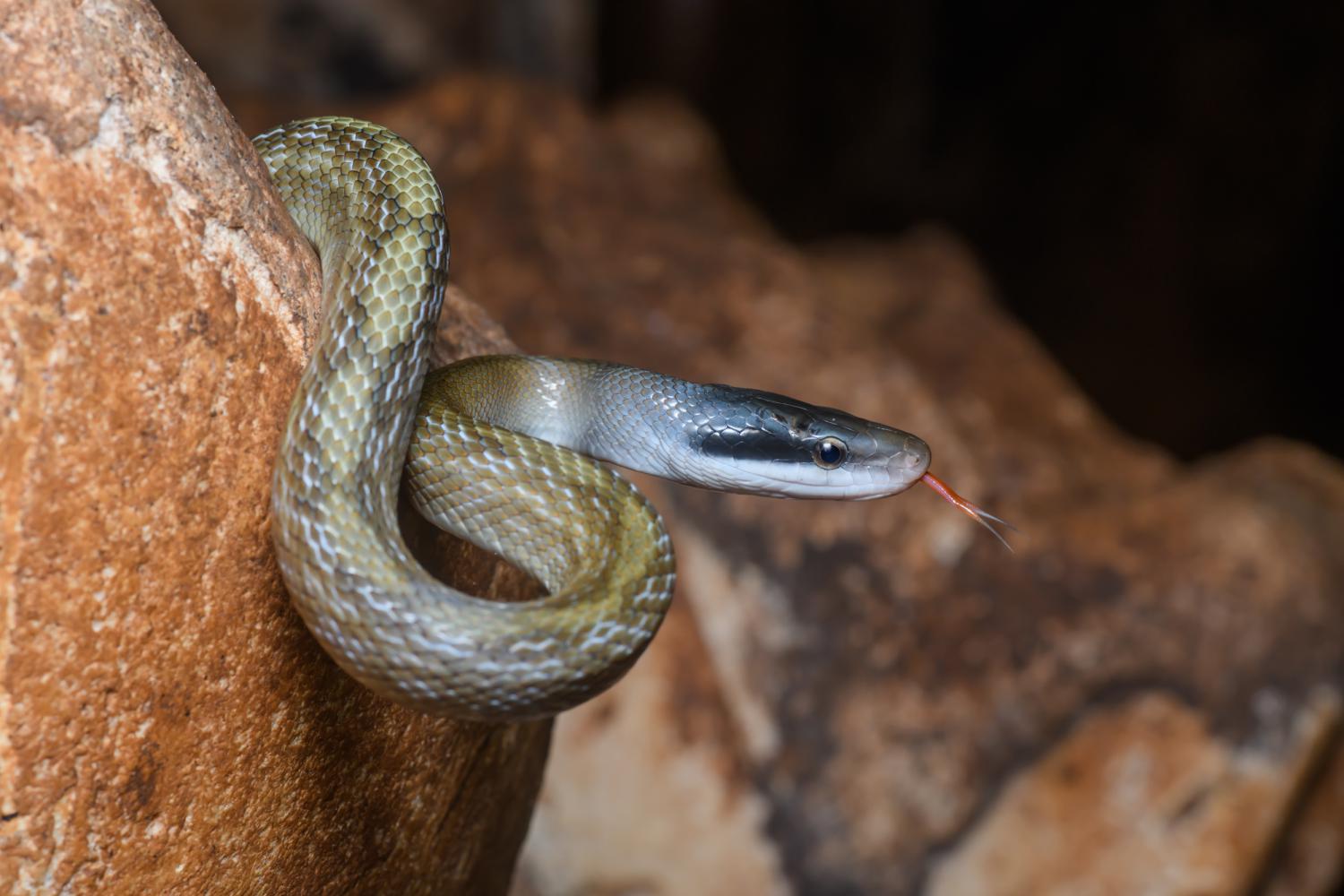
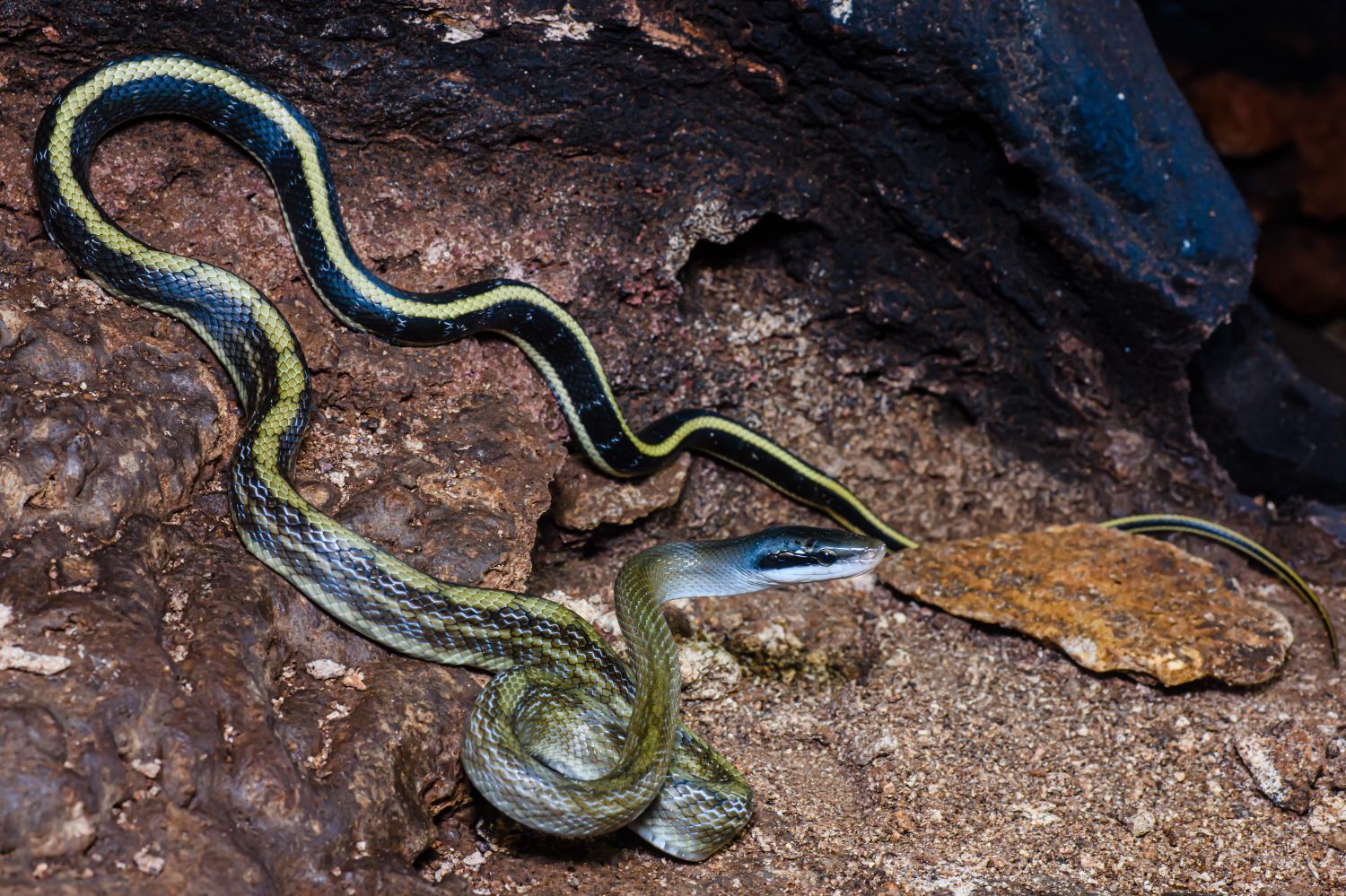
The overall ground color is yellowish-brown to olive, becoming darker at the end of the tail. The skin on the back of the neck and head are uniform in color and the back is typically marked with two pairs of round black spots that meld together. Starting at the back corner of each eye, a black stripe reaches back to each corner of the mouth which is pale cream around the upper labial area.
Subspecies
Subspecies of this species include:
- Chinese beauty snake (Elaphe taeniura taeniura) – Native to China. This subspecies has 11 different morphs.
- Ridley's beauty snake, cave dwelling ratsnake, cave racer (Elaphe taeniura ridleyi) – Native to Thailand and Peninsular Malaysia. Bred in captivity in Cameron Highlands. Is listed as Vulnerable on the China Species Red List. (As the name implies, often lives deep within caves where its diet consists mainly of bats. They have a yellow to beige background color that darkens to a grey-black towards the tail. A white to cream mid-dorsal stripe starts about half of the way down the body and continues to the tip of tail. Both sides of the head are marked just behind the eye with a black stripe surrounded by blue.)
- Mocquard's beauty rat snake (Elaphe taeniura mocquardi) – Native to southeastern China and northern Vietnam, as well as the island of Hainan.
- Taiwan/Taiwanese beauty snake, stripe tail ratsnake (Elaphe taeniura friesei, previously Elaphe taeniura friesi) – Native to Taiwan.
- Vietnamese blue beauty/blue beauty snake (Elaphe taeniura callicyanous) – Native to Vietnam, Cambodia and Thailand.
- Helfenberger's beauty snake (Elaphe taeniura helfenbergeri) – Native to Myanmar and Thailand.
- Elaphe taeniura grabowskyi – Native to Sumatra and the provinces of East Malaysia and Kalimantan on the island of Borneo.
- Elaphe taeniura schmackeri – Native to the Ryukyu Islands of Japan.
- Elaphe taeniura yunnanensis – Native to China, India, Laos, Myanmar, eastern Thailand and Vietnam.
- Elaphe taeniura ssp. – Native to Burma, Thailand and Vietnam.
Etymology
The subspecific name, grabowskyi, is in honor of biologist .
The subspecific name, mocquardi, is in honor of French herpetologist François Mocquard.
Geographic range and habitat
The range of the species covers much of southern and southeastern Asia, excluding western and northeastern China. Within these countries, these snakes can be typically found in rain forests as well as within caves.
Behavior
Due to their preference for caves, beauty snakes have become able climbers and are known to move along cave walls. This ability becomes a strong asset for them when it comes to hunting. In addition, likely due to its cave-dwelling habits, beauty rat snakes are cathemeral, meaning that they are active at random times during the 24-hour day regardless of whether it is day or night outside.
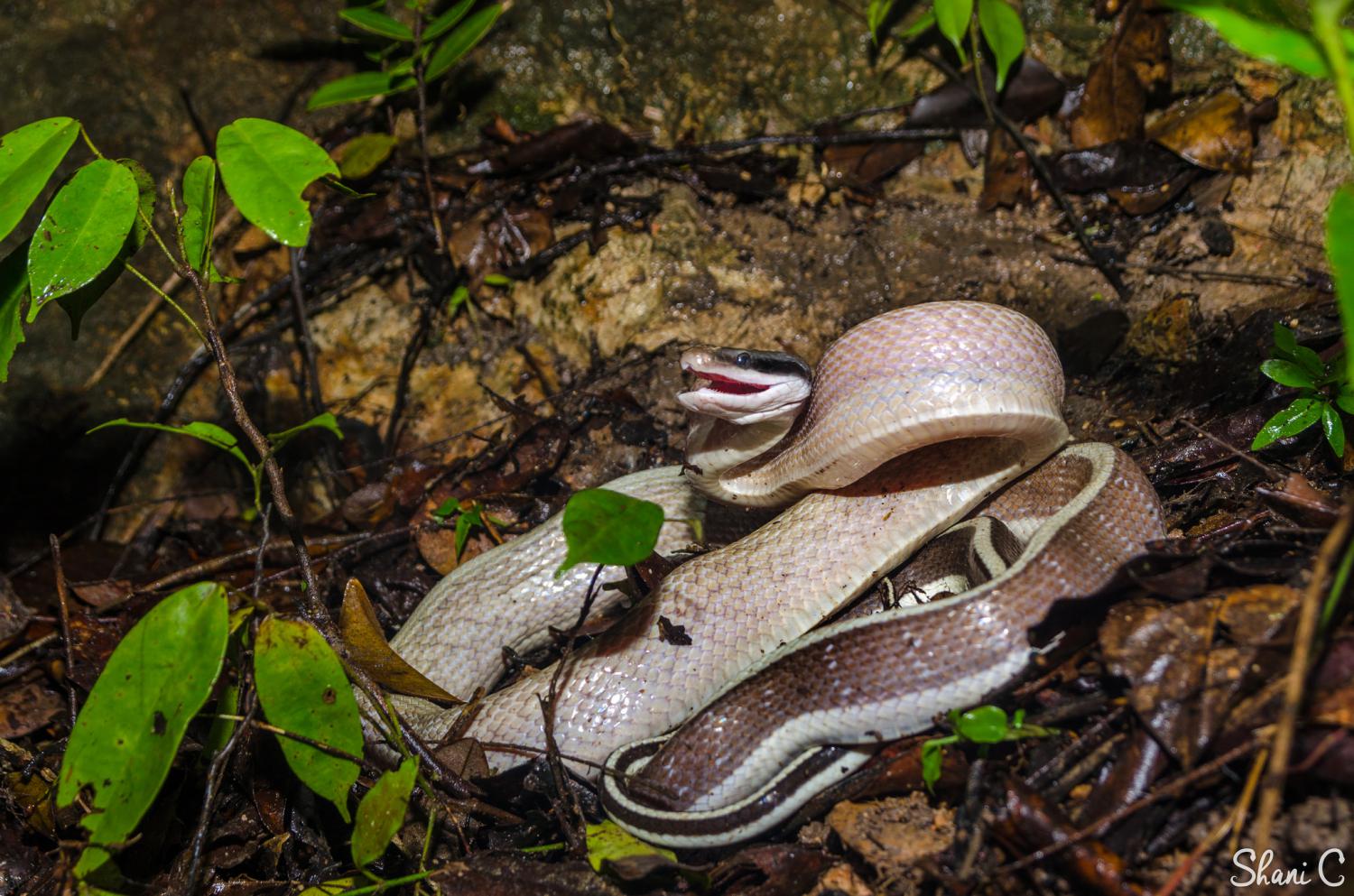
When upset the beauty rat snakes will "waggle" its tail in an attempt to make noises that may scare the source of its fear. Another defensive behavior it exhibits when frightened is to flatten its body vertically in an attempt to look larger or more intimidating.
Feeding
The beauty rat snake typically feeds on ground rodents such as mice and, due to the snake's climbing abilities, even bats that are roosting within the caves they share. In addition to small mammals, beauty rat snakes have also been known to eat birds and bird eggs occasionally.
Breeding
The beauty rat snake species is oviparous, and mating usually results about a month after the hibernation period which is during times when the temperature is around 18 - 20 C F. After laying 4-12 eggs, the female will incubate and defend them for about 70 days, only taking occasional breaks to hunt. Recently hatched young range about 30–45 cm in length. About two weeks later they will begin to shed their first skin. Within the next 14 months, hatchlings grow to be about 135 cm ftin long and are able to breed another 4 months later.
Threats and predators
Though beauty rat snakes are typically in less accessible caves, the top predators of these serpents are birds and mammals.
Interaction with humans
The beauty rat snake is largely traded in the Chinese snake skin and live snake trade. Overall, the Chinese beauty snake, Taiwan beauty snake and Vietnamese blue beauty snake are the most popular of the subspecies to be kept as pets. Pop culture has also been influenced by the beauty rat snake by having Mozler, the main monster from the 1988 Hong Kong film Thunder of Gigantic Serpent, be of the same species. Though Mozler displays a calm temperament, this is seen mainly in captive bred snakes. Wild caught snakes can have difficult dispositions despite being kept as pets for several years.
As an invasive species
Though the overall species is native to Asia, certain subspecies have become invasive in regions of Asia to which they are not local. The cause of their invasion varies but one of the leading causes is individuals that have been transported by the pet trade and escaping or being released by owners. Another reason has been military movement of resources which has created routes along which serpents can move.
On the island of Okinawa one subspecies of beauty rat snake, suspected to be the Taiwanese beauty snake, has been established as an invasive species since the late 1970s. The Taiwanese beauty snake was originally brought onto the islands to be displayed at zoos as well as for medicinal purposes but now has spread through forests and urban locations. According to the article Invasive Species of Japan, the "spread of to northern part of Okinawa Island could threaten endemic and endangered birds and mammals, such as Gallirallus okinawae, Erithacus komadori namiyei, Diplothrix legata, Tokudaia muenninki, etc." As of yet, there is no further published information on the exact impact of the Taiwanese beauty snake's invasion into Okinawa.
Policies and laws
Currently, according to the Invasive Alien Species (IAS) Act, it is illegal in Japan to own, transport or bring any Taiwanese beauty snake into the country. The IAS Act also maintains a list differentiating between Invasive Alien Species (IAS) Uncategorized Alien Species (UAS) and Living Organisms Required to have a Certificate Attached (LORCA) while they are brought into the country. The Taiwanese beauty snake is the only subspecies of beauty rat snake labeled as an IAS. The subspecies Orthiophis taeniurus schmackeri is the only one listed as an exemption of the UAS category but all subspecies (exempting the prohibited Taiwanese beauty snake) classify as LORCAs.
This article uses material from Wikipedia released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike Licence 3.0. Eventual photos shown in this page may or may not be from Wikipedia, please see the license details for photos in photo by-lines.
Scientific classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Subphylum
- Vertebrata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Squamata
- Suborder
- Serpentes
- Family
- Colubridae
- Genus
- Elaphe
- Species
- Elaphe taeniura
Common names
- English:
- Cave racer
- Long-tailed rat snake
- Beauty snake
- Thai:
- งูกาบหมากถ้ำ, ngu gaap maag tham
- งูกาบหมากดำ, ngu gaap maag damm (Ridley’s racer)
- งูกาบหมากยูนนาน, ngu gaap maag Yunaan (Yunnan racer)
Subspecies
Elaphe taeniura callicyanous, Klaus-Dieter Schulz, 2010
Common name: Blue beauty rat snake, Vietnamese blue beauty
Range: Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand
Elaphe taeniura friesi, Werner, 1927
Common name: Taiwan beauty snake, Taiwan beauty rat snake
Range: Taiwan
Elaphe taeniura grabowskyi, Johann Gustav Fischer, 1885
Common name: Grabowsky's beauty snake
Range: Indonesia & Malaysia
Elaphe taeniura helfenbergeri, Klaus-Dieter Schulz, 2010
Common name: Helfenberger's beauty snake
Range: Myanmar, Thailand
Elaphe taeniura mocquardi, Klaus-Dieter Schulz, 1996
Common name: Mocquard's beauty rat snake
Range: China, Vietnam, Thailand
Elaphe taeniura ridleyi, A. Butler, 1899
Common name: Cave-dwelling rat snake, Ridley’s racer
Range: Malaysia, Singapore (?), South Thailand (Up to Kaeng Krachan National Park)
Elaphe taeniura schmackeri, Oskar Boettger, 1895
Common name: Sakishima beauty snake
Range: Japan (Ryukyu Islands).
Elaphe taeniura taeniurus, Edward Drinker Cope, 1861
Common name: Chinese beauty snake
Range: China
Elaphe taeniura yunnanensis, John Anderson, 1879
Common name: Yunnan beauty rat snake
Range: China, India, Laos, Myanmar, Eastern/Northern Thailand and Vietnam
Conservation status
Vulnerable (IUCN 3.1)
Photos
Please help us review our species pages if wrong photos are used or any other details in the page is wrong. We can be reached via our contact us page.
Range Map
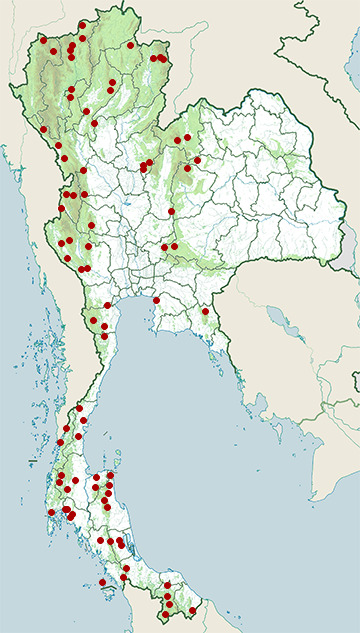
- Ao Luek District, Krabi
- Ban Hong District, Lamphun
- Ban Rai District, Uthai Thani
- Bannang Sata District, Yala
- Betong District, Yala
- Bo Kluea District, Nan
- Chai Prakan District, Chiang Mai
- Chaloem Rattanakosin National Park
- Chiang Dao District, Chiang Mai
- Chiang Dao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Chiang Kham District, Phayao
- Doi Chong National Park
- Doi Pha Hom Pok National Park
- Doi Phu Kha National Park
- Hua Hin District, Prachuap Khiri Khan
- Kaeng Krachan National Park
- Kanchanadit District, Surat Thani
- Khanom District, Nakhon Si Thammarat
- Khao Banthat Wildlife Sanctuary
- Khao Chaison District, Phatthalung
- Khao Luang National Park
- Khao Nan National Park
- Khao Phanom Bencha National Park
- Khao Soi Dao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Khao Sok National Park
- Khao Yoi District, Phetchaburi
- Khiri Rat Nikhom District, Surat Thani
- Khlong Saeng Wildlife Sanctuary
- Khlong Wang Chao National Park
- Khon San District, Chaiyaphum
- Ko Tarutao
- Kra Buri District, Ranong
- Lam Khlong Ngu National Park
- Lam Sonthi District, Lopburi
- Lan Saka District, Nakhon Si Thammarat
- Mae Mo District, Lampang
- Mae Ramat District, Tak
- Mae Sot District, Tak
- Mae Taeng District, Chiang Mai
- Mae Wong National Park
- Muak Lek District, Saraburi
- Mueang Chonburi District, Chonburi
- Mueang Chumphon District, Chumphon
- Mueang Krabi District, Krabi
- Mueang Phatthalung District, Phatthalung
- Mueang Ranong District, Ranong
- Mueang Trang District, Trang
- Mueang Yala District, Yala
- Noen Maprang District, Phitsanulok
- Pa Sang District, Lamphun
- Pai District, Mae Hong Son
- Pak Chong District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Pang Mapha District, Mae Hong Son
- Phanom District, Surat Thani
- Phu Luang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Phu Pha Man National Park
- Pua District, Nan
- Sai Yok District, Kanchanaburi
- Sai Yok National Park
- Salak Pra Wildlife Sanctuary
- Si Satchanalai National Park
- Sichon District, Nakhon Si Thammarat
- Tai Rom Yen National Park
- Takua Thung District, Phang Nga
- Tha Sae District, Chumphon
- Tha Song Yang District, Tak
- Tha Yang District, Phetchaburi
- Thale Ban National Park
- Tham Pha Tha Phon Non-Hunting Area
- Tham Pha Thai National Park
- Than Bok Khorani National Park
- Than To District, Yala
- Thong Pha Phum District, Kanchanaburi
- Thung Salaeng Luang National Park
- Thung Tako District, Chumphon
- Thung Yai Naresuan Wildlife Sanctuary
- Ton Nga-Chang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Umphang District, Tak
- Umphang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Waeng District, Narathiwat
- Wang Saphung District, Loei




